Topical application of L-menthol induces heat analgesia, mechanical allodynia, and a biphasic effect on cold sensitivity in rats
- PMID: 20398704
- PMCID: PMC2882150
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2010.04.015
Topical application of L-menthol induces heat analgesia, mechanical allodynia, and a biphasic effect on cold sensitivity in rats
Abstract
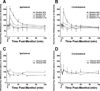
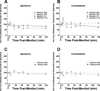
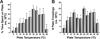
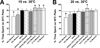
Menthol is used in analgesic balms and also in foods and oral hygiene products for its fresh cooling sensation. Menthol enhances cooling by interacting with the cold-sensitive thermoTRP channel TRPM8, but its effect on pain is less well understood. We presently used behavioral methods to investigate effects of topical menthol on thermal (hot and cold) pain and innocuous cold and mechanical sensitivity in rats. Menthol dose-dependently increased the latency for noxious heat-evoked withdrawal of the treated hindpaw with a weak mirror-image effect, indicating antinociception. Menthol at the highest concentration (40%) reduced mechanical withdrawal thresholds, with no effect at lower concentrations. Menthol had a biphasic effect on cold avoidance. At high concentrations (10% and 40%) menthol reduced avoidance of colder temperatures (15 degrees C and 20 degrees C) compared to 30 degrees C, while at lower concentrations (0.01-1%) menthol enhanced cold avoidance. In a -5 degrees C cold plate test, 40% menthol significantly increased the nocifensive response latency (cold hypoalgesia) while lower concentrations were not different from vehicle controls. These results are generally consistent with neurophysiological and human psychophysical data and support TRPM8 as a potential peripheral target of pain modulation.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Somatosensory and vasomotor manifestations of individual and combined stimulation of TRPM8 and TRPA1 using topical L-menthol and trans-cinnamaldehyde in healthy volunteers.Eur J Pain. 2014 Oct;18(9):1333-42. doi: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2014.494.x. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Eur J Pain. 2014. PMID: 24664788 Clinical Trial.
-
Topical hindpaw application of L-menthol decreases responsiveness to heat with biphasic effects on cold sensitivity of rat lumbar dorsal horn neurons.Neuroscience. 2012 Sep 6;219:234-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.05.061. Epub 2012 Jun 9. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22687951 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of iPLA2, TRPM8 and TRPA1 in chemically induced cold hypersensitivity.Mol Pain. 2010 Jan 21;6:4. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-4. Mol Pain. 2010. PMID: 20092626 Free PMC article.
-
The role and mechanism of action of menthol in topical analgesic products.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2018 Jun;43(3):313-319. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12679. Epub 2018 Mar 10. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2018. PMID: 29524352 Review.
-
A review of topical high-concentration L-menthol as a translational model of cold allodynia and hyperalgesia.Eur J Pain. 2014 Mar;18(3):315-25. doi: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2013.00380.x. Epub 2013 Aug 20. Eur J Pain. 2014. PMID: 23963768 Review.
Cited by
-
TRPM8 and Migraine.Headache. 2016 Oct;56(9):1406-1417. doi: 10.1111/head.12948. Epub 2016 Sep 16. Headache. 2016. PMID: 27634619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role and Function of TRPM8 in the Digestive System.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 21;14(7):877. doi: 10.3390/biom14070877. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel menthol-derived cooling compounds activate primary and second-order trigeminal sensory neurons and modulate lingual thermosensitivity.Chem Senses. 2011 Sep;36(7):649-58. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjr029. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Chem Senses. 2011. PMID: 21511802 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of nefopam on streptozotocin-induced diabetic neuropathic pain in rats.Korean J Pain. 2014 Oct;27(4):326-33. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.4.326. Epub 2014 Oct 1. Korean J Pain. 2014. PMID: 25317281 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the transport of QX-314 through TRPA1, TRPM8, and TRPV1 channels.J Pain Res. 2013;6:223-30. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S41614. Epub 2013 Mar 16. J Pain Res. 2013. PMID: 23525210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe J, Hosokawa H, Sawada Y, Matsumura K, Kobayashi S. Ca2+-dependent PKC activation mediates menthol-induced desensitization of transient receptor potential M8. Neurosci Lett. 2006;397:140–144. - PubMed
-
- Albin KC, Carstens MI, Carstens E. Modulation of oral heat and cold pain by irritant chemicals. Chem Sens. 2008;33:3–15. - PubMed
-
- Bautista DM, Siemens J, Glazer JM, Tsuruda PR, Basbaum AI, Stucky CL, Jordt S-E, Julius D. The menthol receptor TRPM8 is the principal detector of environmental cold. Nature. 2007;448:204–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

