HIV Nef-M1 Effects on Colorectal Cancer Growth in Tumor-induced Spleens and Hepatic Metastasis
- PMID: 20383296
- PMCID: PMC2851221
- DOI: 10.4255/mcpharmacol.09.10
HIV Nef-M1 Effects on Colorectal Cancer Growth in Tumor-induced Spleens and Hepatic Metastasis
Abstract
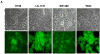
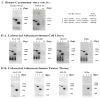
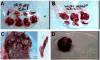
CXCR4 receptors have been implicated in tumorigenesis and proliferation, making it a potential target for colorectal cancer therapy. Expression of this chemokine receptor on cellular surfaces appears to promote metastasis by directly stimulating tumor cell migration and invasion. The receptor/ligand, CXCR4/SDF-1alpha, pair are critically important to angiogenesis and vascular remodeling which supports cancer proliferation. Our work has shown that a novel apoptotic peptide of HIV-1, Nef-M1, can act as a CXCR4 antagonist, inducing apoptosis in CXCR4 containing cells. Four colorectal tumor cell lines (HT-29, LS174t, SW480, WiDr), were evaluated for their response to Nef-M1 peptide via in vivo and in vitro. The presence of CXCR4 receptors on tumor cells was determined using immunohistochemical and RT-PCR analyses. Solid xenografts derived from tumor cell lines grown in SCID mice, were evaluated for the persistence of the receptor. Xenografts propagated in SCID mice from each of the four cell lines demonstrated high levels of receptor expression as well. The effects of Nef-M1 in vivo via splenic injected mice and subsequent hepatic metastasis also demonstrated dramatic reduction of primary tumor growth in the spleen and secondary invasion of the liver. We concluded that Nef-M1 peptide, through physical interaction(s) with CXCR4, drives apoptotic reduction in in vivo primary tumor growth and metastasis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nef-M1, a peptide antagonist of CXCR4, inhibits tumor angiogenesis and epithelial‑to‑mesenchymal transition in colon and breast cancers.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 29;6(29):27763-77. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4615. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26318034 Free PMC article.
-
Nef-M1, a CXCR4 Peptide Antagonist, Enhances Apoptosis and Inhibits Primary Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Breast Cancer.J Cancer Ther. 2013 Jun;4(4):898-906. doi: 10.4236/jct.2013.44101. J Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 25285238 Free PMC article.
-
Stromal cell-derived factor-1α and macrophage migration-inhibitory factor induce metastatic behavior in CXCR4-expressing colon cancer cells.Int J Mol Med. 2012 Dec;30(6):1537-43. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.1141. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Int J Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 23023114
-
A Lentiviral CXCR4 overexpression and knockdown model in colorectal cancer cell lines reveals plerixafor-dependent suppression of SDF-1α-induced migration and invasion.Onkologie. 2011;34(10):502-8. doi: 10.1159/000332390. Epub 2011 Sep 20. Onkologie. 2011. PMID: 21985848
-
Stromal cell-derived factor-1 and CXCR4 receptor interaction in tumor growth and metastasis of breast cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2006 Jul;60(6):273-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2006.06.004. Epub 2006 Jun 28. Biomed Pharmacother. 2006. PMID: 16828253 Review.
Cited by
-
Nef-M1, a peptide antagonist of CXCR4, inhibits tumor angiogenesis and epithelial‑to‑mesenchymal transition in colon and breast cancers.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 29;6(29):27763-77. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4615. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26318034 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecule CXCR4 antagonists block the HIV-1 Nef/CXCR4 axis and selectively initiate the apoptotic program in breast cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2018 Feb 26;9(24):16996-17013. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24580. eCollection 2018 Mar 30. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29682200 Free PMC article.
-
Nef-M1, a CXCR4 Peptide Antagonist, Enhances Apoptosis and Inhibits Primary Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Breast Cancer.J Cancer Ther. 2013 Jun;4(4):898-906. doi: 10.4236/jct.2013.44101. J Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 25285238 Free PMC article.
-
Secretion modification region-derived peptide blocks exosome release and mediates cell cycle arrest in breast cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 14;8(7):11302-11315. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14513. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28076321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nicolson GL. Paracrine and autocrine growth mechanisms in tumor metastasis to specific sites with particular emphasis on brain and lung metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1993;12:325–43. - PubMed
-
- Liang Z, Wu T, Lou H, et al. Inhibition of breast cancer metastasis by selective synthetic polypeptide against CXCR4. Cancer Res. 2004;64:4302–8. - PubMed
-
- Salvucci O, Yao L, Villalba S, Sajewicz A, Pittaluga S, Tosato G. Regulation of endothelial cell branching morphogenesis by endogenous chemokine stromal-derived factor-1. Blood. 2002;99:2703–11. - PubMed
-
- Dewan MZ, Ahmed S, Iwasaki Y, Ohba K, Toi M, Yamamoto N. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 and CXCR4 receptor interaction in tumor growth and metastasis of breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2006;60:273–6. - PubMed
-
- Federsppiel B, Melhado IG, Duncan AM, et al. Molecular cloning of the cDNA and chromosomal localization of the gene for a putative seventransmembrane segment (7-TMS) receptor isolated from human spleen. Genomics. 1993;16:707–12. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
