Epithelial stress and apoptosis underlie Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome-associated interstitial pneumonia
- PMID: 20378731
- PMCID: PMC2913235
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200909-1414OC
Epithelial stress and apoptosis underlie Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome-associated interstitial pneumonia
Abstract
Rationale: The molecular mechanisms underlying Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome-associated interstitial pneumonia (HPSIP) are poorly understood but, as in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, may be linked to chronic alveolar epithelial type II cell (AECII) injury.
Objectives: We studied the development of fibrosis and the role of AECII injury in various murine models of HPS.
Methods: HPS1, HPS2, and HPS6 monomutant mice, and HPS1/2 and HPS1/6 double-mutant and genetic background mice, were killed at 3 and 9 months of age. Quantitative morphometry was undertaken in lung sections stained with hemalaun-eosin. The extent of lung fibrosis was assessed by trichrome staining and hydroxyproline measurement. Surfactant lipids were analyzed by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Surfactant proteins, apoptosis, and lysosomal and endoplasmic reticulum stress markers were studied by Western blotting and immunohistochemistry. Cell proliferation was measured by water-soluble tetrazolium salt-1 and bromodeoxyuridine assays.
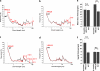
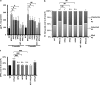
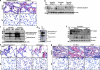
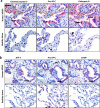
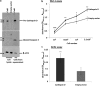
Measurements and main results: Spontaneous and slowly progressive HPSIP was observed in HPS1/2 double mutants, but not in other HPS mutants, with subpleural onset at 3 months and full-blown fibrosis at 9 months. In these mice, extensive surfactant abnormalities were encountered in AECII and were paralleled by early lysosomal stress (cathepsin D induction), late endoplasmic reticulum stress (activating transcription factor-4 [ATF4], C/EBP homologous protein [CHOP] induction), and marked apoptosis. These findings were fully corroborated in human HPSIP. In addition, cathepsin D overexpression resulted in apoptosis of MLE-12 cells and increased proliferation of NIH 3T3 fibroblasts incubated with conditioned medium of the transfected cells.
Conclusions: Extensively impaired surfactant trafficking and secretion underlie lysosomal and endoplasmic reticulum stress with apoptosis of AECII in HPSIP, thereby causing the development of HPSIP.
Figures


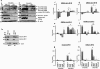

Similar articles
-
MAP1LC3B overexpression protects against Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type-1-induced defective autophagy in vitro.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016 Mar 15;310(6):L519-31. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00213.2015. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26719147 Free PMC article.
-
Altered surfactant homeostasis and alveolar epithelial cell stress in amiodarone-induced lung fibrosis.Toxicol Sci. 2014 Nov;142(1):285-97. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu177. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Toxicol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25163675
-
Early alveolar epithelial dysfunction promotes lung inflammation in a mouse model of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Aug 15;184(4):449-58. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201011-1882OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011. PMID: 21616998 Free PMC article.
-
Disorders of vesicles of lysosomal lineage: the Hermansky-Pudlak syndromes.Curr Mol Med. 2002 Aug;2(5):451-67. doi: 10.2174/1566524023362357. Curr Mol Med. 2002. PMID: 12125811 Review.
-
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome: vesicle formation from yeast to man.Pigment Cell Res. 2002 Dec;15(6):405-19. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0749.2002.02074.x. Pigment Cell Res. 2002. PMID: 12453182 Review.
Cited by
-
Chitinase 3-like-1 and its receptors in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome-associated lung disease.J Clin Invest. 2015 Aug 3;125(8):3178-92. doi: 10.1172/JCI79792. Epub 2015 Jun 29. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 26121745 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Regulation of macroautophagy in amiodarone-induced pulmonary fibrosis.J Pathol Clin Res. 2015 Jun 3;1(4):252-63. doi: 10.1002/cjp2.20. eCollection 2015 Oct. J Pathol Clin Res. 2015. PMID: 27499909 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic studies provide clues on the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Dis Model Mech. 2013 Jan;6(1):9-17. doi: 10.1242/dmm.010736. Dis Model Mech. 2013. PMID: 23268535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of SMARCA4 impairs alveolar epithelial type II cells proliferation and aggravates pulmonary fibrosis in mice.Genes Dis. 2017 Oct 25;4(4):204-214. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2017.10.001. eCollection 2017 Dec. Genes Dis. 2017. PMID: 30258924 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Fibrosis from Genetic Diseases.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022 Jul;67(1):20-35. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2021-0557TR. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35294321 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hermansky F, Pudlak P. Albinism associated with hemorrhagic diathesis and unusual pigmented reticular cells in the bone marrow: report of two cases with histochemical studies. Blood 1959;14:162–169. - PubMed
-
- Li W, Rusiniak ME, Chintala S, Gautam R, Novak EK, Swank RT. Murine Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome genes: regulators of lysosome-related organelles. Bioessays 2004;26:616–628. - PubMed
-
- Huizing M, Gahl WA. Disorders of vesicles of lysosomal lineage: the Hermansky-Pudlak syndromes. Curr Mol Med 2002;2:451–467. - PubMed
-
- Anderson PD, Huizing M, Claassen DA, White J, Gahl WA. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 4 (HPS-4): clinical and molecular characteristics. Hum Genet 2003;113:10–17. - PubMed
-
- Wei ML. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome: a disease of protein trafficking and organelle function. Pigment Cell Res 2006;19:19–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

