Potent and selective fluoroketone inhibitors of group VIA calcium-independent phospholipase A2
- PMID: 20369880
- PMCID: PMC2865582
- DOI: 10.1021/jm901872v
Potent and selective fluoroketone inhibitors of group VIA calcium-independent phospholipase A2
Abstract
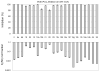
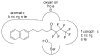
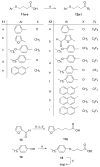
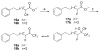
Group VIA calcium-independent phospholipase A(2) (GVIA iPLA(2)) has recently emerged as a novel pharmaceutical target. We have now explored the structure-activity relationship between fluoroketones and GVIA iPLA(2) inhibition. The presence of a naphthyl group proved to be of paramount importance. 1,1,1-Trifluoro-6-(naphthalen-2-yl)hexan-2-one (FKGK18) is the most potent inhibitor of GVIA iPLA(2) (X(I)(50) = 0.0002) ever reported. Being 195 and >455 times more potent for GVIA iPLA(2) than for GIVA cPLA(2) and GV sPLA(2), respectively, makes it a valuable tool to explore the role of GVIA iPLA(2) in cells and in vivo models. 1,1,1,2,2,3,3-Heptafluoro-8-(naphthalene-2-yl)octan-4-one inhibited GVIA iPLA(2) with a X(I)(50) value of 0.001 while inhibiting the other intracellular GIVA cPLA(2) and GV sPLA(2) at least 90 times less potently. Hexa- and octafluoro ketones were also found to be potent inhibitors of GVIA iPLA(2); however, they are not selective.
Figures
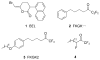
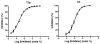
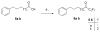
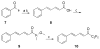
Similar articles
-
New potent and selective polyfluoroalkyl ketone inhibitors of GVIA calcium-independent phospholipase A2.Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Sep 15;21(18):5823-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.07.010. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23916152 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular phospholipase A(2) group IVA and group VIA play important roles in Wallerian degeneration and axon regeneration after peripheral nerve injury.Brain. 2008 Oct;131(Pt 10):2620-31. doi: 10.1093/brain/awn188. Epub 2008 Aug 21. Brain. 2008. PMID: 18718965 Free PMC article.
-
Differential inhibition of group IVA and group VIA phospholipases A2 by 2-oxoamides.J Med Chem. 2006 May 4;49(9):2821-8. doi: 10.1021/jm050993h. J Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16640343 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase A2 biochemistry.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2009 Feb;23(1):49-59. doi: 10.1007/s10557-008-6132-9. Epub 2008 Oct 18. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2009. PMID: 18931897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular basis of unique specificity and regulation of group VIA calcium-independent phospholipase A2 (PNPLA9) and its role in neurodegenerative diseases.Pharmacol Ther. 2023 May;245:108395. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108395. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 36990122 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Potent and Selective Inhibitors for Group VIA Calcium-Independent Phospholipase A2 Guided by Molecular Dynamics and Structure-Activity Relationships.J Med Chem. 2016 May 12;59(9):4403-14. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00377. Epub 2016 Apr 28. J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27087127 Free PMC article.
-
β-Lactones: A Novel Class of Ca2+-Independent Phospholipase A2 (Group VIA iPLA2) Inhibitors with the Ability To Inhibit β-Cell Apoptosis.J Med Chem. 2019 Mar 28;62(6):2916-2927. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01216. Epub 2019 Mar 12. J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30798607 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipid Arachidonic Acid Remodeling During Phagocytosis in Mouse Peritoneal Macrophages.Biomedicines. 2020 Aug 5;8(8):274. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8080274. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32764331 Free PMC article.
-
Highly Potent 2-Oxoester Inhibitors of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 (GIVA cPLA2).ACS Omega. 2018 Aug 31;3(8):8843-8853. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b01214. Epub 2018 Aug 9. ACS Omega. 2018. PMID: 30197994 Free PMC article.
-
Insertion of the Ca²⁺-independent phospholipase A₂ into a phospholipid bilayer via coarse-grained and atomistic molecular dynamics simulations.PLoS Comput Biol. 2013;9(7):e1003156. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003156. Epub 2013 Jul 25. PLoS Comput Biol. 2013. PMID: 23935474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schaloske RH, Dennis EA. The phospholipase A(2) superfamily and its group numbering system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1761:1246–1259. - PubMed
-
- Leslie CC. Regulation of the specific release of arachidonic acid by cytosolic phospholipase A2. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2004;70:373–376. - PubMed
-
- Mounier CM, Ghomashchi F, Lindsay MR, James S, Singer AG, Parton RG, Gelb MH. Arachidonic acid release from mammalian cells transfected with human groups IIA and X secreted phospholipase A2 occurs predominantly during the secretory process and with the involvement of cytosolic phospholipase A2-α. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:25024–25038. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

