Astrocyte-restricted ablation of interleukin-17-induced Act1-mediated signaling ameliorates autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 20303295
- PMCID: PMC3073618
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.03.004
Astrocyte-restricted ablation of interleukin-17-induced Act1-mediated signaling ameliorates autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
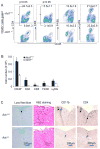
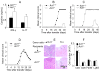
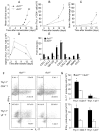
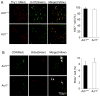
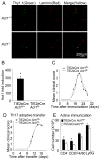
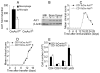
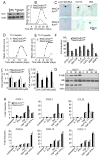
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) secreted by T helper 17 (Th17) cells is essential in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). However, it remains unclear how IL-17-mediated signaling in different cellular compartments participates in the central nervous system (CNS) inflammatory process. We examined CNS inflammation in mice with specific deletion of Act1, a critical component required for IL-17 signaling, in endothelial cells, macrophages and microglia, and neuroectoderm (neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes). In Act1-deficient mice, Th17 cells showed normal infiltration into the CNS but failed to recruit lymphocytes, neutrophils, and macrophages. Act1 deficiency in endothelial cells or in macrophages and microglia did not substantially impact the development of EAE. However, targeted Act1 deficiency in neuroectoderm-derived CNS-resident cells resulted in markedly reduced severity in EAE. Specifically, Act1-deficient astrocytes showed impaired IL-17-mediated inflammatory gene induction. Thus, astroctyes are critical in IL-17-Act1-mediated leukocyte recruitment during autoimmune-induced inflammation of the CNS.
Figures
Comment in
-
Act1, scene brain: astrocytes play a lead role.Immunity. 2010 Mar 26;32(3):302-4. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.03.009. Immunity. 2010. PMID: 20346771 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Act1, scene brain: astrocytes play a lead role.Immunity. 2010 Mar 26;32(3):302-4. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.03.009. Immunity. 2010. PMID: 20346771 Free PMC article.
-
CNS-specific therapy for ongoing EAE by silencing IL-17 pathway in astrocytes.Mol Ther. 2012 Jul;20(7):1338-48. doi: 10.1038/mt.2012.12. Epub 2012 Mar 20. Mol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22434134 Free PMC article.
-
RKIP mediates autoimmune inflammation by positively regulating IL-17R signaling.EMBO Rep. 2018 Jun;19(6):e44951. doi: 10.15252/embr.201744951. Epub 2018 Apr 19. EMBO Rep. 2018. PMID: 29674348 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17 receptor signaling and T helper 17-mediated autoimmune demyelinating disease.Trends Immunol. 2011 May;32(5):232-9. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2011.02.007. Epub 2011 Apr 12. Trends Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21493143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translational mini-review series on Th17 cells: are T helper 17 cells really pathogenic in autoimmunity?Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Feb;159(2):131-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.04039.x. Epub 2009 Nov 11. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 19912250 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Control of IL-17 receptor signaling and tissue inflammation by the p38α-MKP-1 signaling axis in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis.Sci Signal. 2015 Mar 3;8(366):ra24. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaa2147. Sci Signal. 2015. PMID: 25737586 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of IL-17 in autoimmune diseases by transcriptional factors and microRNAs.Front Genet. 2015 Jul 14;6:236. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00236. eCollection 2015. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 26236331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CNS-targeted production of IL-17A induces glial activation, microvascular pathology and enhances the neuroinflammatory response to systemic endotoxemia.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57307. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057307. Epub 2013 Feb 27. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23468966 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte barriers to neurotoxic inflammation.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015 May;16(5):249-63. doi: 10.1038/nrn3898. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25891508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRAF3IP2, a novel therapeutic target in glioblastoma multiforme.Oncotarget. 2018 Jul 3;9(51):29772-29788. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25710. eCollection 2018 Jul 3. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30038719 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrawal A, Dillon S, Denning TL, Pulendran B. ERK1−/− mice exhibit Th1 cell polarization and increased susceptibility to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2006;176:5788–5796. - PubMed
-
- Aloisi F. Immune function of microglia. Glia. 2001;36:165–179. - PubMed
-
- Awane M, Andres PG, Li DJ, Reinecker HC. NF-kappa B-inducing kinase is a common mediator of IL-17-, TNF-alpha-, and IL-1 beta-induced chemokine promoter activation in intestinal epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1999;162:5337–5344. - PubMed
-
- Becher B, Bechmann I, Greter M. Antigen presentation in autoimmunity and CNS inflammation: how T lymphocytes recognize the brain. J Mol Med. 2006;84:532–543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

