Phylogenetic analysis of fungal ABC transporters
- PMID: 20233411
- PMCID: PMC2848647
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-177
Phylogenetic analysis of fungal ABC transporters
Abstract
Background: The superfamily of ABC proteins is among the largest known in nature. Its members are mainly, but not exclusively, involved in the transport of a broad range of substrates across biological membranes. Many contribute to multidrug resistance in microbial pathogens and cancer cells. The diversity of ABC proteins in fungi is comparable with those in multicellular animals, but so far fungal ABC proteins have barely been studied.
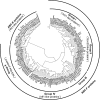
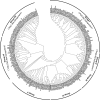
Results: We performed a phylogenetic analysis of the ABC proteins extracted from the genomes of 27 fungal species from 18 orders representing 5 fungal phyla thereby covering the most important groups. Our analysis demonstrated that some of the subfamilies of ABC proteins remained highly conserved in fungi, while others have undergone a remarkable group-specific diversification. Members of the various fungal phyla also differed significantly in the number of ABC proteins found in their genomes, which is especially reduced in the yeast S. cerevisiae and S. pombe.
Conclusions: Data obtained during our analysis should contribute to a better understanding of the diversity of the fungal ABC proteins and provide important clues about their possible biological functions.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Diversity and evolution of ABC proteins in basidiomycetes.Mycologia. 2013 Nov-Dec;105(6):1456-70. doi: 10.3852/13-001. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Mycologia. 2013. PMID: 23928421
-
Diversity and evolution of ABC proteins in mycorrhiza-forming fungi.BMC Evol Biol. 2015 Dec 28;15:249. doi: 10.1186/s12862-015-0526-7. BMC Evol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26707138 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary Trajectories of Entomopathogenic Fungi ABC Transporters.Adv Genet. 2017;98:117-154. doi: 10.1016/bs.adgen.2017.07.002. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Adv Genet. 2017. PMID: 28942792 Review.
-
Exploring the biological roles of Dothideomycetes ABC proteins: Leads from their phylogenetic relationships with functionally-characterized Ascomycetes homologs.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 2;13(8):e0197447. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197447. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30071023 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily in vertebrates.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2005;6:123-42. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genom.6.080604.162122. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2005. PMID: 16124856 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of virulence associated milRNAs and their bidirectional targets in Rhizoctonia solani and maize during infection.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Mar 26;21(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-02930-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 33771101 Free PMC article.
-
Differential contributions of five ABC transporters to mutidrug resistance, antioxidion and virulence of Beauveria bassiana, an entomopathogenic fungus.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 15;8(4):e62179. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062179. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23596534 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of ABC transporter genes of Fusarium graminearum with roles in azole tolerance and/or virulence.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 11;8(11):e79042. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079042. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24244413 Free PMC article.
-
A putative ABC transporter gene, ZRA1, is required for zearalenone production in Gibberella zeae.Curr Genet. 2011 Oct;57(5):343-51. doi: 10.1007/s00294-011-0352-4. Epub 2011 Aug 11. Curr Genet. 2011. PMID: 21833740
-
The Structure and Mechanism of Drug Transporters.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2342:193-234. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1554-6_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34272696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ABCISSE database (ABC systems: Information on Sequence, Structure and Evolution) http://www1.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/pmtg/abc/database.iphtml
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

