Genomic definition of multiple ex vivo regulatory T cell subphenotypes
- PMID: 20231436
- PMCID: PMC2851866
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1002006107
Genomic definition of multiple ex vivo regulatory T cell subphenotypes
Abstract
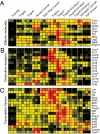
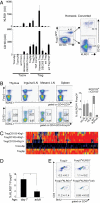
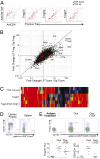
Regulatory T (Treg) cells that express the Foxp3 transcription factor are essential for lymphoid homeostasis and immune tolerance to self. Other nonimmunological functions of Treg cells, such as controlling metabolic function in adipose tissue, are also emerging. Treg cells originate primarily in the thymus, but can also be elicited from conventional T cells by in vivo exposure to low-dose antigen or homeostatic expansion or by activation in the presence of TGFbeta in vitro. Treg cells are characterized by a distinct transcriptional signature controlled in part, but not solely, by Foxp3. For a better perspective on transcriptional control in Treg cells, we compared gene expression profiles of a broad panel of Treg cells from various origins or anatomical locations. Treg cells generated by different means form different subphenotypes and were identifiable by particular combinations of transcripts, none of which fully encompassed the entire Treg signature. Molecules involved in Treg cell effector function, chemokine receptors, and the transcription factors that control them were differentially represented in these subphenotypes. Treg cells from the gut proved dissimilar to cells elicited by exposure to TGFbeta in vitro, but instead they resembled a CD103(+)Klrg1(+) subphenotype preferentially generated in response to lymphopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells are dispensable for controlling CD8+ T cell-mediated lung inflammation.J Immunol. 2011 Jun 1;186(11):6106-18. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000632. Epub 2011 Apr 25. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21518973
-
IL-2Rβ-dependent signaling and CD103 functionally cooperate to maintain tolerance in the gut mucosa.J Immunol. 2015 Feb 1;194(3):1334-46. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400955. Epub 2014 Dec 19. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25527788 Free PMC article.
-
CD103 is a hallmark of tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells.Int J Cancer. 2011 Nov 15;129(10):2417-26. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25902. Epub 2011 Apr 1. Int J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21207371
-
Mechanisms of foxp3+ T regulatory cell-mediated suppression.Immunity. 2009 May;30(5):636-45. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.04.010. Immunity. 2009. PMID: 19464986 Review.
-
Expanding and converting regulatory T cells: a horizon for immunotherapy.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2009 May-Jun;57(3):199-204. doi: 10.1007/s00005-009-0021-1. Epub 2009 May 29. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2009. PMID: 19479206 Review.
Cited by
-
Phenotypic and functional properties of Helios+ regulatory T cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e34547. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034547. Epub 2012 Mar 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22479644 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T cells control NK cells in an insulitic lesion by depriving them of IL-2.J Exp Med. 2013 Jun 3;210(6):1153-65. doi: 10.1084/jem.20122248. Epub 2013 May 6. J Exp Med. 2013. PMID: 23650440 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T Cells in Tumor-Associated Tertiary Lymphoid Structures Suppress Anti-tumor T Cell Responses.Immunity. 2015 Sep 15;43(3):579-90. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.08.006. Epub 2015 Sep 1. Immunity. 2015. PMID: 26341400 Free PMC article.
-
HTLV-1 bZIP Factor Impairs Anti-viral Immunity by Inducing Co-inhibitory Molecule, T Cell Immunoglobulin and ITIM Domain (TIGIT).PLoS Pathog. 2016 Jan 6;12(1):e1005372. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005372. eCollection 2016 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 26735971 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T cells characterized by low Id3 expression are highly suppressive and accumulate during chronic infection.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 27;8(61):102835-102851. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22159. eCollection 2017 Nov 28. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29262527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zheng Y, Rudensky AY. Foxp3 in control of the regulatory T cell lineage. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:457–462. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell. 2008;133:775–787. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S, et al. Foxp3+ CD25+ CD4+ natural regulatory T cells in dominant self-tolerance and autoimmune disease. Immunol Rev. 2006;212:8–27. - PubMed
-
- Belkaid Y, Tarbell K. Regulatory T cells in the control of host-microorganism interactions (*) Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:551–589. - PubMed
-
- O'Garra A, Vieira P. T(H)1 cells control themselves by producing interleukin-10. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:425–428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

