Regulation of Lrp6 phosphorylation
- PMID: 20229235
- PMCID: PMC11115861
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0329-3
Regulation of Lrp6 phosphorylation
Abstract
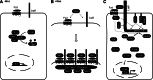
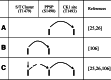
The Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway plays important roles in embryonic development and tissue homeostasis, and is implicated in human disease. Wnts transduce signals via transmembrane receptors of the Frizzled (Fzd/Fz) family and the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6 (Lrp5/6). A key mechanism in their signal transduction is that Wnts induce Lrp6 signalosomes, which become phosphorylated at multiple conserved sites, notably at PPSPXS motifs. Lrp6 phosphorylation is crucial to beta-catenin stabilization and pathway activation by promoting Axin and Gsk3 recruitment to phosphorylated sites. Here, we summarize how proline-directed kinases (Gsk3, PKA, Pftk1, Grk5/6) and non-proline-directed kinases (CK1 family) act upon Lrp6, how the phosphorylation is regulated by ligand binding and mitosis, and how Lrp6 phosphorylation leads to beta-catenin stabilization.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of GSK3 phosphorylation of beta-catenin via phosphorylated PPPSPXS motifs of Wnt coreceptor LRP6.PLoS One. 2009;4(3):e4926. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004926. Epub 2009 Mar 18. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19293931 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases promote WNT/beta-catenin signaling via phosphorylation of LRP6.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jan;31(1):179-89. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00550-10. Epub 2010 Oct 25. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 20974802 Free PMC article.
-
Initiation of Wnt signaling: control of Wnt coreceptor Lrp6 phosphorylation/activation via frizzled, dishevelled and axin functions.Development. 2008 Jan;135(2):367-75. doi: 10.1242/dev.013540. Epub 2007 Dec 12. Development. 2008. PMID: 18077588 Free PMC article.
-
LDL receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: arrows point the way.Development. 2004 Apr;131(8):1663-77. doi: 10.1242/dev.01117. Development. 2004. PMID: 15084453 Review.
-
LRPs in WNT Signalling.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021;269:45-73. doi: 10.1007/164_2021_526. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34490514 Review.
Cited by
-
The CK1δ/ε-AES axis regulates tumorigenesis and metastasis in colorectal cancer.Theranostics. 2021 Mar 4;11(9):4421-4435. doi: 10.7150/thno.53901. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33754069 Free PMC article.
-
More Favorable Palmitic Acid Over Palmitoleic Acid Modification of Wnt3 Ensures Its Localization and Activity in Plasma Membrane Domains.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Nov 15;7:281. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00281. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31803740 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt Signaling in Heart Development and Regeneration.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2022 Oct;24(10):1425-1438. doi: 10.1007/s11886-022-01756-8. Epub 2022 Aug 4. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35925512 Review.
-
The Novel Secreted Adipokine WNT1-inducible Signaling Pathway Protein 2 (WISP2) Is a Mesenchymal Cell Activator of Canonical WNT.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 7;289(10):6899-6907. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.511964. Epub 2014 Jan 22. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24451367 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of valvular and vascular sclerosis by osteogenic morphogens.Circ Res. 2011 Aug 19;109(5):564-77. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.234278. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21852555 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell. 2006;127:469–480. - PubMed
-
- Logan CY, Nusse R. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:781–810. - PubMed
-
- Klaus A, Birchmeier W. Wnt signalling and its impact on development and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:387–398. - PubMed
-
- van Amerongen R, Mikels A, Nusse R (2008) Alternative Wnt Signaling Is Initiated by Distinct Receptors. Sci Signal 1, re9 - PubMed
-
- Gordon MD, Nusse R. Wnt signaling: multiple pathways, multiple receptors, and multiple transcription factors. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:22429–22433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

