Programmed death-1-induced interleukin-10 production by monocytes impairs CD4+ T cell activation during HIV infection
- PMID: 20208540
- PMCID: PMC4229134
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2106
Programmed death-1-induced interleukin-10 production by monocytes impairs CD4+ T cell activation during HIV infection
Abstract
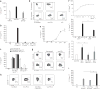
Viral replication and microbial translocation from the gut to the blood during HIV infection lead to hyperimmune activation, which contributes to the decline in CD4+ T cell numbers during HIV infection. Programmed death-1 (PD-1) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) are both upregulated during HIV infection. Blocking interactions between PD-1 and programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) and between IL-10 and IL-10 receptor (IL-10R) results in viral clearance and improves T cell function in animal models of chronic viral infections. Here we show that high amounts of microbial products and inflammatory cytokines in the plasma of HIV-infected subjects lead to upregulation of PD-1 expression on monocytes that correlates with high plasma concentrations of IL-10. Triggering of PD-1 expressed on monocytes by PD-L1 expressed on various cell types induced IL-10 production and led to reversible CD4+ T cell dysfunction. We describe a new function for PD-1 whereby microbial products inhibit T cell expansion and function by upregulating PD-1 levels and IL-10 production by monocytes after binding of PD-1 by PD-L1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


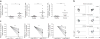

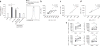
Similar articles
-
Differential impact of PD-1 and/or interleukin-10 blockade on HIV-1-specific CD4 T cell and antigen-presenting cell functions.J Virol. 2014 Mar;88(5):2508-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02034-13. Epub 2013 Dec 18. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24352453 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory molecules that regulate expansion and restoration of HCV-specific CD4+ T cells in patients with chronic infection.Gastroenterology. 2011 Oct;141(4):1422-31, 1431.e1-6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.004. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Gastroenterology. 2011. PMID: 21763239
-
The common gamma-chain cytokines IL-2, IL-7, IL-15, and IL-21 induce the expression of programmed death-1 and its ligands.J Immunol. 2008 Nov 15;181(10):6738-46. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.10.6738. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18981091
-
The inhibitory co-receptors: a way to save from anergy the HIV-specific T cells.Curr HIV Res. 2009 May;7(3):266-72. doi: 10.2174/157016209788347949. Curr HIV Res. 2009. PMID: 19442121 Review.
-
Dissecting How CD4 T Cells Are Lost During HIV Infection.Cell Host Microbe. 2016 Mar 9;19(3):280-91. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.02.012. Cell Host Microbe. 2016. PMID: 26962940 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune Suppression by Myeloid Cells in HIV Infection: New Targets for Immunotherapy.Open AIDS J. 2014 Dec 29;8:66-78. doi: 10.2174/1874613601408010066. eCollection 2014. Open AIDS J. 2014. PMID: 25624956 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular signatures of T-cell inhibition in HIV-1 infection.Retrovirology. 2013 Mar 20;10:31. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-10-31. Retrovirology. 2013. PMID: 23514593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Programmed cell death-1 single-nucleotide polymorphism rs10204525 is associated with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA viral load in HIV-1-infected Moroccan subjects.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2021 Aug;210(4):187-196. doi: 10.1007/s00430-021-00712-7. Epub 2021 May 24. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34031715
-
Clinical blockade of PD1 and LAG3--potential mechanisms of action.Nat Rev Immunol. 2015 Jan;15(1):45-56. doi: 10.1038/nri3790. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25534622 Review.
-
IL-21 induces antiviral microRNA-29 in CD4 T cells to limit HIV-1 infection.Nat Commun. 2015 Jun 25;6:7562. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8562. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26108174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El-Far M, et al. T-cell exhaustion in HIV infection. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2008;5:13–19. - PubMed
-
- Klenerman P, Hill A. T cells and viral persistence: lessons from diverse infections. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:873–879. - PubMed
-
- Brenchley JM, et al. Microbial translocation is a cause of systemic immune activation in chronic HIV infection. Nat Med. 2006;12:1365–1371. - PubMed
-
- Breen EC, et al. Infection with HIV is associated with elevated IL-6 levels and production. J Immunol. 1990;144:480–484. - PubMed
-
- Chollet-Martin S, et al. Comparison of plasma cytokine levels in African patients with HIV-1 and HIV-2 infection. AIDS. 1994;8:879–884. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

