Mutations in the bile acid biosynthetic enzyme sterol 27-hydroxylase underlie cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis
- PMID: 2019602
- PMCID: PMC4449724
Mutations in the bile acid biosynthetic enzyme sterol 27-hydroxylase underlie cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis
Abstract
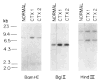
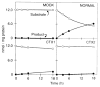
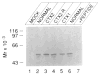
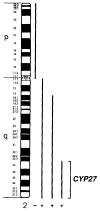
The sterol storage disorder cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX) is characterized by abnormal deposition of cholesterol and cholestanol in multiple tissues. Deposition in the central nervous system leads to neurological dysfunction marked by dementia, spinal cord paresis, and cerebellar ataxia. Deposition in other tissues causes tendon xanthomas, premature atherosclerosis, and cataracts. In two unrelated patients with CTX, we have identified different point mutations in the gene (CYP27) encoding sterol 27-hydroxylase, a key enzyme in the bile acid biosynthesis pathway. Transfection of mutant cDNAs into cultured cells results in the synthesis of immunoreactive sterol 27-hydroxylase protein with greatly diminished enzyme activity. We have localized the CYP27 gene to the q33-qter interval of human chromosome 2, and to mouse chromosome 1, in agreement with the autosomal recessive inheritance pattern of CTX. These findings underscore the essential role played by sterols in the central nervous system and suggest that mutations in other sterol metabolizing enzymes may contribute to diseases with neurological manifestations.
Figures

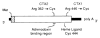
Similar articles
-
A novel mutation in the cytochrome P450(27) (CYP27) gene caused cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis in a Japanese family.J Lipid Res. 1996 Mar;37(3):631-9. J Lipid Res. 1996. PMID: 8728324
-
A point mutation in the bile acid biosynthetic enzyme sterol 27-hydroxylase in a family with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis.J Lipid Res. 1994 Apr;35(4):663-8. J Lipid Res. 1994. PMID: 8006521
-
Identification of new mutations in sterol 27-hydroxylase gene in Japanese patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX).J Lipid Res. 1994 Jun;35(6):1031-9. J Lipid Res. 1994. PMID: 7915755
-
Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis.Curr Opin Lipidol. 1994 Apr;5(2):138-42. doi: 10.1097/00041433-199404000-00010. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1994. PMID: 8044416 Review.
-
Clinical and molecular diagnosis of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis with a review of the mutations in the CYP27A1 gene.Neurol Sci. 2006 Jun;27(2):143-9. doi: 10.1007/s10072-006-0618-7. Neurol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16816916 Review.
Cited by
-
Activity of 25-hydroxylase in human gingival fibroblasts and periodontal ligament cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52053. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052053. Epub 2012 Dec 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23251684 Free PMC article.
-
The safety and effectiveness of chenodeoxycholic acid treatment in patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: two retrospective cohort studies.Neurol Sci. 2020 Apr;41(4):943-949. doi: 10.1007/s10072-019-04169-8. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Neurol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31863326 Free PMC article.
-
Autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxias.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2006 Nov 17;1:47. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-1-47. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2006. PMID: 17112370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage lipid accumulation in the presence of immunosuppressive drugs mycophenolate mofetil and cyclosporin A.Inflamm Res. 2019 Sep;68(9):787-799. doi: 10.1007/s00011-019-01262-8. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Inflamm Res. 2019. PMID: 31227843
-
Nationwide survey on cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis in Japan.J Hum Genet. 2018 Mar;63(3):271-280. doi: 10.1038/s10038-017-0389-4. Epub 2018 Jan 10. J Hum Genet. 2018. PMID: 29321515
References
-
- Myant NB. The Biology of Cholesterol and Related Steroids. Heinemann Medical Books; London: 1981. pp. 1–910.
-
- Norton WT. In: Basic Neurochemistry. 2. Siegel GJ, Albers RW, Katzman R, Agranoff BW, editors. Little, Brown and Co; Boston: 1976. pp. 74–99.
-
- Van Bogaert L, Scherer HJ, Epstein E. Une Forme Cerebrale De La Cholesterinose Generalisee. Masson; Paris: 1937. pp. 1–159.
-
- Bjorkhem I, Skrede S. In: The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease. 6. Scriber CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, editors. McGraw-Hill Book Co; New York: 1989. pp. 1283–1302.
-
- Menkes JH, Schimschock JR, Swanson PD. Arch Neurol. 1968;19:47–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

