Ribosomal protein L11 associates with c-Myc at 5 S rRNA and tRNA genes and regulates their expression
- PMID: 20194507
- PMCID: PMC2857078
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.056259
Ribosomal protein L11 associates with c-Myc at 5 S rRNA and tRNA genes and regulates their expression
Erratum in
- J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 10;285(50):39574
Abstract
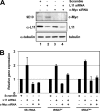
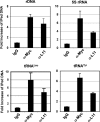
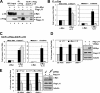
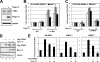
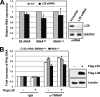
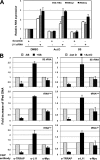
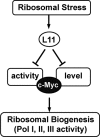
The c-Myc oncoprotein promotes cell growth by enhancing ribosomal biogenesis. Overexpression of c-Myc and aberrant ribosomal biogenesis lead to deregulated cell growth and tumorigenesis. Hence, c-Myc activity and ribosomal biogenesis must be tightly coordinated during normal homeostasis. We previously found that ribosomal protein L11 inhibits c-Myc activity by blocking the recruitment of its co-activator transformation/transcription domain-associated protein (TRRAP) to the promoter regions of c-Myc target genes that are transcribed by RNA polymerases I and II. In this study, we extended the role of L11 to the regulation of c-Myc-driven transcription of the 5 S rRNA and tRNA genes by RNA polymerase III. L11 co-resided with c-Myc at the 5 S rRNA and tRNA genes and significantly inhibited the binding of TRRAP to these genes. Knocking down endogenous L11 enhanced c-Myc-dependent transcription of these genes. Interestingly, in response to ribosomal stress induced by the treatment of cells with a low dose of actinomycin D or serum starvation, L11 binding to these genes was increased, and inversely TRRAP binding to these genes was decreased. Consistently, knockdown of L11 rescued the reduction of the expression of these genes by the two treatments. These results demonstrate that L11 suppresses c-Myc-dependent and RNA polymerase III-catalyzed transcription of 5 S rRNA and tRNA genes in response to ribosomal stress, ensuring a tight coordination between c-Myc activity and ribosomal biogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of c-Myc activity by ribosomal protein L11.EMBO J. 2007 Jul 25;26(14):3332-45. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601776. Epub 2007 Jun 28. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17599065 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal protein L11 recruits miR-24/miRISC to repress c-Myc expression in response to ribosomal stress.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Oct;31(19):4007-21. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05810-11. Epub 2011 Aug 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21807902 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal protein S14 negatively regulates c-Myc activity.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 26;288(30):21793-801. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.445122. Epub 2013 Jun 17. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23775087 Free PMC article.
-
Feedback regulation of c-Myc by ribosomal protein L11.Cell Cycle. 2007 Nov 15;6(22):2735-41. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.22.4895. Epub 2007 Aug 14. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 18032916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation by c-Myc of transcription by RNA polymerases I, II and III.Biochem Soc Symp. 2006;(73):141-54. doi: 10.1042/bss0730141. Biochem Soc Symp. 2006. PMID: 16626295 Review.
Cited by
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of BRG1 by FIRΔexon2 in gastric cancer.Oncogenesis. 2020 Feb 18;9(2):26. doi: 10.1038/s41389-020-0205-4. Oncogenesis. 2020. PMID: 32071290 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding motif protein 10 inactivates c-Myc by partnering with ribosomal proteins uL18 and uL5.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Dec 5;120(49):e2308292120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2308292120. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 38032932 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal proteins and human diseases: pathogenesis, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic implications.Med Res Rev. 2015 Mar;35(2):225-85. doi: 10.1002/med.21327. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Med Res Rev. 2015. PMID: 25164622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer-specific alterations in nuclear matrix proteins determined by multi-omics analyses of ductal carcinoma in situ.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 6;14:1406946. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1406946. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39165691 Free PMC article.
-
An extensive network of information flow through the B1b/c intersubunit bridge of the yeast ribosome.PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e20048. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020048. Epub 2011 May 19. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21625514 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

