Rituximab specifically depletes short-lived autoreactive plasma cells in a mouse model of inflammatory arthritis
- PMID: 20176942
- PMCID: PMC2842072
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1001074107
Rituximab specifically depletes short-lived autoreactive plasma cells in a mouse model of inflammatory arthritis
Abstract
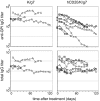
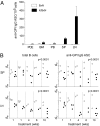
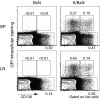
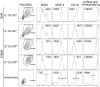
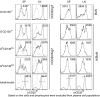
There is increasing appreciation of the important role of B cells in many autoimmune diseases and consequently, increasing interest in treating these disorders through B cell-depletion therapy with rituximab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody. Yet, precisely how this and related drugs exert their therapeutic effects remains controversial. In particular, it is unclear how, in a number of contexts, rituximab can greatly reduce the titer of serum autoantibodies without substantially altering the overall antibody titer. We have studied the action of this drug in the K/BxN mouse model of inflammatory arthritis after first crossing in a human CD20 transgene. Rituximab treatment of these mice led to a decrease in the titer of serum antibodies targeting glucose-6-phosphate isomerase, the relevant autoantigen, but not in the total antibody titer. Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase-specific plasma cells did not reside primarily in the bone marrow as expected but rather in the spleen and lymph nodes, where they had short lives, expressed CD20, and were rapidly depleted by rituximab. These data support a model whereby autoreactive plasma cells (at least certain specificities thereof) are intrinsically different from protective antimicrobial plasma cells in their differentiation, migration, and survival properties. Rituximab targets the former and spares the latter.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

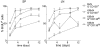
Comment in
-
Rituximab targets short-lived autoreactive plasmablasts.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010 May;6(5):246. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2010.53. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20440898 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Expanded CD23(+)/CD21(hi) B cells in inflamed lymph nodes are associated with the onset of inflammatory-erosive arthritis in TNF-transgenic mice and are targets of anti-CD20 therapy.J Immunol. 2010 Jun 1;184(11):6142-50. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903489. Epub 2010 Apr 30. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20435928 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of specific anti-B and/or anti-plasma cell immunotherapy on antibody production in baboons: depletion of CD20- and CD22-positive B cells does not result in significantly decreased production of anti-alphaGal antibody.Xenotransplantation. 2001 Aug;8(3):157-71. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3089.2001.008003157.x. Xenotransplantation. 2001. PMID: 11472623
-
Long-term B cell depletion in murine lupus eliminates autoantibody-secreting cells and is associated with alterations in the kidney plasma cell niche.J Immunol. 2014 Apr 1;192(7):3011-20. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302003. Epub 2014 Feb 26. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24574498 Free PMC article.
-
B-cell: a logical target for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007 Mar-Apr;25(2):318-28. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 17543163 Review.
-
The role and clinical implications of G6PI in experimental models of rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(1):20-8. doi: 10.1186/ar1476. Epub 2004 Nov 30. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. PMID: 15642150 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Autoantibody depletion ameliorates disease in murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.MAbs. 2013 Sep-Oct;5(5):655-9. doi: 10.4161/mabs.25439. Epub 2013 Jun 19. MAbs. 2013. PMID: 23846320 Free PMC article.
-
Combination therapy for inhibitor reversal in haemophilia A using monoclonal anti-CD20 and rapamycin.Thromb Haemost. 2017 Jan 5;117(1):33-43. doi: 10.1160/TH16-05-0404. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 27683758 Free PMC article.
-
A Glance on Nanovaccine: A Potential Approach for Disease Prevention.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024;25(11):1406-1418. doi: 10.2174/0113892010254221231006100659. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37861010 Review.
-
TACI deletion protects against progressive murine lupus nephritis induced by BAFF overexpression.Kidney Int. 2018 Oct;94(4):728-740. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.03.012. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Kidney Int. 2018. PMID: 29907458 Free PMC article.
-
Immunology of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome.Pediatr Nephrol. 2018 Apr;33(4):573-584. doi: 10.1007/s00467-017-3677-5. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 28451893 Review.
References
-
- Martin F, Chan AC. B cell immunobiology in disease: Evolving concepts from the clinic. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:467–496. - PubMed
-
- Hoyer BF, Manz RA, Radbruch A, Hiepe F. Long-lived plasma cells and their contribution to autoimmunity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1050:124–133. - PubMed
-
- Radbruch A, et al. Competence and competition: The challenge of becoming a long-lived plasma cell. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:741–750. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

