The SUMO E3 ligase activity of Pc2 is coordinated through a SUMO interaction motif
- PMID: 20176810
- PMCID: PMC2863578
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01510-09
The SUMO E3 ligase activity of Pc2 is coordinated through a SUMO interaction motif
Abstract
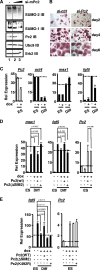
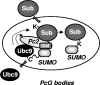
Protein modification by SUMO conjugation has emerged to be an important regulatory event. Recently, the mechanisms through which SUMO elicits its effects on target proteins have been elucidated. One of these is the noncovalent association between SUMO and coregulatory proteins via SUMO interaction motifs (SIMs). We therefore searched for additional binding proteins to elucidate how SUMO acts as a signal to potentiate novel noncovalent interactions with SUMO-binding proteins. We identified an E3 ligase, Pc2, as a SUMO-binding protein with two functionally distinct SIMs. Here, we focus on the role of SIM2 and demonstrate that it is crucial for many of the documented Pc2 functions, which converge on determining its E3 ligase activity. One role of SUMO binding in this context is the subnuclear partitioning of the active form of Ubc9 (SUMO approximately Ubc9) by Pc2. The significance of the SIM2-dependent functions of Pc2 is demonstrated in the control of the precise expression of lineage-specific genes during embryonic stem cell differentiation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A role for non-covalent SUMO interaction motifs in Pc2/CBX4 E3 activity.PLoS One. 2010 Jan 20;5(1):e8794. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008794. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20098713 Free PMC article.
-
MEL-18 interacts with HSF2 and the SUMO E2 UBC9 to inhibit HSF2 sumoylation.J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 21;283(12):7464-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707122200. Epub 2008 Jan 21. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18211895 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation-dependent control of Pc2 SUMO E3 ligase activity by its substrate protein HIPK2.Mol Cell. 2006 Oct 6;24(1):77-89. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.08.004. Mol Cell. 2006. PMID: 17018294
-
Pc2 and SUMOylation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Dec;35(Pt 6):1401-4. doi: 10.1042/BST0351401. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 18031231 Review.
-
SUMO: getting it on.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Dec;35(Pt 6):1409-13. doi: 10.1042/BST0351409. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 18031233 Review.
Cited by
-
Arkadia, a novel SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase involved in PML degradation.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jun;33(11):2163-77. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01019-12. Epub 2013 Mar 25. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23530056 Free PMC article.
-
E2s: structurally economical and functionally replete.Biochem J. 2011 Jan 1;433(1):31-42. doi: 10.1042/BJ20100985. Biochem J. 2011. PMID: 21158740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of sumoylation in the regulation of actin, microtubules, intermediate filaments, and septins.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2015 Jul;72(7):305-39. doi: 10.1002/cm.21226. Epub 2015 Aug 22. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2015. PMID: 26033929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Entropy-driven mechanism of an E3 ligase.Biochemistry. 2011 Jun 28;50(25):5757-66. doi: 10.1021/bi2001856. Epub 2011 Jun 3. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21568279 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle RING-finger protein-1 (MuRF1) functions and cellular localization are regulated by SUMO1 post-translational modification.J Mol Cell Biol. 2019 May 1;11(5):356-370. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjy036. J Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 29868881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baba, D., N. Maita, J. G. Jee, Y. Uchimura, H. Saitoh, K. Sugasawa, F. Hanaoka, H. Tochio, H. Hiroaki, and M. Shirakawa. 2005. Crystal structure of thymine DNA glycosylase conjugated to SUMO-1. Nature 435:979-982. - PubMed
-
- Bossis, G., and F. Melchior. 2006. Regulation of SUMOylation by reversible oxidation of SUMO conjugating enzymes. Mol. Cell 21:349-357. - PubMed
-
- Cão, R., Y. Tsukada, and Y. Zhang. 2005. Role of Bmi-1 and Ring1A in H2A ubiquitylation and Hox gene silencing. Mol. Cell 20:845-854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
