Circadian rhythms and metabolic syndrome: from experimental genetics to human disease
- PMID: 20167942
- PMCID: PMC2837358
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.208355
Circadian rhythms and metabolic syndrome: from experimental genetics to human disease
Abstract
The incidence of the metabolic syndrome represents a spectrum of disorders that continue to increase across the industrialized world. Both genetic and environmental factors contribute to metabolic syndrome and recent evidence has emerged to suggest that alterations in circadian systems and sleep participate in the pathogenesis of the disease. In this review, we highlight studies at the intersection of clinical medicine and experimental genetics that pinpoint how perturbations of the internal clock system, and sleep, constitute risk factors for disorders including obesity, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, thrombosis and even inflammation. An exciting aspect of the field has been the integration of behavioral and physiological approaches, and the emerging insight into both neural and peripheral tissues in disease pathogenesis. Consideration of the cell and molecular links between disorders of circadian rhythms and sleep with metabolic syndrome has begun to open new opportunities for mechanism-based therapeutics.
Figures
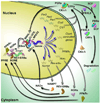
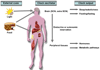
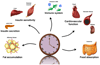
Similar articles
-
Circadian disruption in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome.Diabetes Metab. 2014 Nov;40(5):338-46. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2013.12.005. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Diabetes Metab. 2014. PMID: 24433933 Review.
-
Clock genes in hypertension: novel insights from rodent models.Blood Press Monit. 2014 Oct;19(5):249-54. doi: 10.1097/MBP.0000000000000060. Blood Press Monit. 2014. PMID: 25025868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Chronobiological aspects of obesity and metabolic syndrome].Endocrinol Nutr. 2012 Jan;59(1):50-61. doi: 10.1016/j.endonu.2011.08.002. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Endocrinol Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22100640 Review. Spanish.
-
[Importance of sleep and circadian rhythm for energy metabolism].Internist (Berl). 2019 Feb;60(2):122-127. doi: 10.1007/s00108-018-0543-x. Internist (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30645664 Review. German.
-
Circadian rhythms, sleep, and metabolism.J Clin Invest. 2011 Jun;121(6):2133-41. doi: 10.1172/JCI46043. Epub 2011 Jun 1. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21633182 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Leptin-sensitive neurons in the arcuate nuclei contribute to endogenous feeding rhythms.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012 Jun;302(11):R1313-26. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00086.2012. Epub 2012 Apr 4. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22492818 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models of in utero exposure to a high fat diet: a review.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Mar;1842(3):507-519. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.07.006. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23872578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dawn-to-dusk dry fasting induces anti-atherosclerotic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumorigenic proteome in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in subjects with metabolic syndrome.Metabol Open. 2022 Nov 1;16:100214. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2022.100214. eCollection 2022 Dec. Metabol Open. 2022. PMID: 36506940 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro characterisation of murine pre-adipose nucleated cells reveals electrophysiological cycles associated with biological clocks.Electrophoresis. 2022 Jun;43(12):1337-1346. doi: 10.1002/elps.202100308. Epub 2022 May 22. Electrophoresis. 2022. PMID: 35543378 Free PMC article.
-
Shift work and the risk for metabolic syndrome among healthcare workers: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Obes Rev. 2022 Oct;23(10):e13489. doi: 10.1111/obr.13489. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Obes Rev. 2022. PMID: 35734805 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lorenzo C, Williams K, Hunt KJ, Haffner SM. The National Cholesterol Education Program - Adult Treatment Panel III, International Diabetes Federation, and World Health Organization definitions of the metabolic syndrome as predictors of incident cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:8–13. - PubMed
-
- Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J. The metabolic syndrome--a new worldwide definition. Lancet. 2005;366:1059–1062. - PubMed
-
- Klein S, Allison DB, Heymsfield SB, Kelley DE, Leibel RL, Nonas C, Kahn R. Waist circumference and cardiometabolic risk: a consensus statement from shaping America's health: Association for Weight Management and Obesity Prevention; NAASO, the Obesity Society; the American Society for Nutrition; and the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:1647–1652. - PubMed
-
- Zimmet P, Magliano D, Matsuzawa Y, Alberti G, Shaw J. The metabolic syndrome: a global public health problem and a new definition. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2005;12:295–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

