Active site remodelling accompanies thioester bond formation in the SUMO E1
- PMID: 20164921
- PMCID: PMC2866016
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08765
Active site remodelling accompanies thioester bond formation in the SUMO E1
Abstract
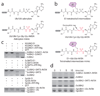
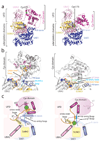
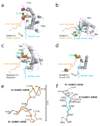
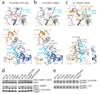
E1 enzymes activate ubiquitin (Ub) and ubiquitin-like (Ubl) proteins in two steps by carboxy-terminal adenylation and thioester bond formation to a conserved catalytic cysteine in the E1 Cys domain. The structural basis for these intermediates remains unknown. Here we report crystal structures for human SUMO E1 in complex with SUMO adenylate and tetrahedral intermediate analogues at 2.45 and 2.6 A, respectively. These structures show that side chain contacts to ATP.Mg are released after adenylation to facilitate a 130 degree rotation of the Cys domain during thioester bond formation that is accompanied by remodelling of key structural elements including the helix that contains the E1 catalytic cysteine, the crossover and re-entry loops, and refolding of two helices that are required for adenylation. These changes displace side chains required for adenylation with side chains required for thioester bond formation. Mutational and biochemical analyses indicate these mechanisms are conserved in other E1s.
Figures


Comment in
-
Structural biology: Transformative encounters.Nature. 2010 Feb 18;463(7283):889-90. doi: 10.1038/463889a. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20164915 No abstract available.
-
And yet it moves: active site remodeling in the SUMO E1.Structure. 2010 Mar 14;18(4):419-21. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2010.03.005. Structure. 2010. PMID: 20399179
Similar articles
-
Domain alternation and active site remodeling are conserved structural features of ubiquitin E1.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jul 21;292(29):12089-12099. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.787622. Epub 2017 Jun 1. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28572513 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for adenylation and thioester bond formation in the ubiquitin E1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jul 30;116(31):15475-15484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1905488116. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31235585 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of the SUMO E1 provide mechanistic insights into SUMO activation and E2 recruitment to E1.EMBO J. 2005 Feb 9;24(3):439-51. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600552. Epub 2005 Jan 20. EMBO J. 2005. PMID: 15660128 Free PMC article.
-
Protein interactions in the sumoylation cascade: lessons from X-ray structures.FEBS J. 2008 Jun;275(12):3003-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06459.x. Epub 2008 May 17. FEBS J. 2008. PMID: 18492068 Review.
-
DeSUMOylating enzymes--SENPs.IUBMB Life. 2008 Nov;60(11):734-42. doi: 10.1002/iub.113. IUBMB Life. 2008. PMID: 18666185 Review.
Cited by
-
Decoding the messaging of the ubiquitin system using chemical and protein probes.Cell Chem Biol. 2021 Jul 15;28(7):889-902. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2021.03.009. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Cell Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 33831368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tracking of Ubiquitin Signaling through 3.5 Billion Years of Combinatorial Conjugation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 8;25(16):8671. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168671. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macromolecular juggling by ubiquitylation enzymes.BMC Biol. 2013 Jun 25;11:65. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-11-65. BMC Biol. 2013. PMID: 23800009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CacyBP/SIP protein is sumoylated in neuroblastoma NB2a cells.Neurochem Res. 2013 Nov;38(11):2427-32. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1155-4. Neurochem Res. 2013. PMID: 24078263 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Based Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Non-Acyl Sulfamate Inhibitors of the Adenylate-Forming Enzyme MenE.Biochemistry. 2019 Apr 9;58(14):1918-1930. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00003. Epub 2019 Mar 26. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 30912442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnson ES. Protein modification by SUMO. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:355–382. - PubMed
-
- Melchior F. SUMO--nonclassical ubiquitin. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2000;16:591–626. - PubMed
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:425–479. - PubMed
-
- Laney JD, Hochstrasser M. Substrate targeting in the ubiquitin system. Cell. 1999;97(4):427–430. - PubMed
-
- Dye BT, Schulman BA. Structural mechanisms underlying posttranslational modification by ubiquitin-like proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2007;36:131–150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

