Accurate SNP and mutation detection by targeted custom microarray-based genomic enrichment of short-fragment sequencing libraries
- PMID: 20164091
- PMCID: PMC2879533
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq072
Accurate SNP and mutation detection by targeted custom microarray-based genomic enrichment of short-fragment sequencing libraries
Abstract
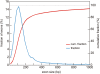
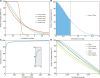
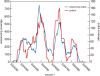
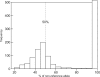
Microarray-based enrichment of selected genomic loci is a powerful method for genome complexity reduction for next-generation sequencing. Since the vast majority of exons in vertebrate genomes are smaller than 150 nt, we explored the use of short fragment libraries (85-110 bp) to achieve higher enrichment specificity by reducing carryover and adverse effects of flanking intronic sequences. High enrichment specificity (60-75%) was obtained with a relative even base coverage. Up to 98% of the target-sequence was covered more than 20x at an average coverage depth of about 200x. To verify the accuracy of SNP/mutation detection, we evaluated 384 known non-reference SNPs in the targeted regions. At approximately 200x average sequence coverage, we were able to survey 96.4% of 1.69 Mb of genomic sequence with only 4.2% false negative calls, mostly due to low coverage. Using the same settings, a total of 1197 novel candidate variants were detected. Verification experiments revealed only eight false positive calls, indicating an overall false positive rate of less than 1 per approximately 200,000 bp. Taken together, short fragment libraries provide highly efficient and flexible enrichment of exonic targets and yield relatively even base coverage, which facilitates accurate SNP and mutation detection. Raw sequencing data, alignment files and called SNPs have been submitted into GEO database http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/ with accession number GSE18542.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Population-based rare variant detection via pooled exome or custom hybridization capture with or without individual indexing.BMC Genomics. 2012 Dec 6;13:683. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-683. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23216810 Free PMC article.
-
Massively parallel sequencing of ataxia genes after array-based enrichment.Hum Mutat. 2010 Apr;31(4):494-9. doi: 10.1002/humu.21221. Hum Mutat. 2010. PMID: 20151403
-
Performance of microarray and liquid based capture methods for target enrichment for massively parallel sequencing and SNP discovery.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 9;6(2):e16486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016486. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21347407 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of solution-based exome capture methods for next generation sequencing.Genome Biol. 2011 Sep 28;12(9):R94. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-9-r94. Genome Biol. 2011. PMID: 21955854 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted enrichment of genomic DNA regions for next-generation sequencing.Brief Funct Genomics. 2011 Nov;10(6):374-86. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elr033. Epub 2011 Nov 26. Brief Funct Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22121152 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Next generation diagnostics in inherited arrhythmia syndromes : a comparison of two approaches.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2013 Feb;6(1):94-103. doi: 10.1007/s12265-012-9401-8. Epub 2012 Sep 7. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2013. PMID: 22956155 Free PMC article.
-
Using a priori knowledge to align sequencing reads to their exact genomic position.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Sep;40(16):e125. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks393. Epub 2012 May 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22581774 Free PMC article.
-
Next generation sequence analysis and computational genomics using graphical pipeline workflows.Genes (Basel). 2012 Aug 30;3(3):545-75. doi: 10.3390/genes3030545. Genes (Basel). 2012. PMID: 23139896 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic DNA pooling strategy for next-generation sequencing-based rare variant discovery in abdominal aortic aneurysm regions of interest-challenges and limitations.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2011 Jun;4(3):271-80. doi: 10.1007/s12265-011-9263-5. Epub 2011 Mar 1. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2011. PMID: 21360310 Free PMC article.
-
Chromothripsis is a common mechanism driving genomic rearrangements in primary and metastatic colorectal cancer.Genome Biol. 2011 Oct 19;12(10):R103. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-10-r103. Genome Biol. 2011. PMID: 22014273 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

