Overlapping and distinct role of CXCR7-SDF-1/ITAC and CXCR4-SDF-1 axes in regulating metastatic behavior of human rhabdomyosarcomas
- PMID: 20162608
- PMCID: PMC2907445
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.25245
Overlapping and distinct role of CXCR7-SDF-1/ITAC and CXCR4-SDF-1 axes in regulating metastatic behavior of human rhabdomyosarcomas
Abstract
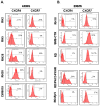
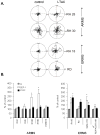
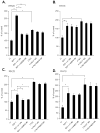
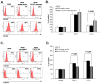
We have demonstrated that the α-chemokine stromal-derived factor (SDF)-1-CXCR4 axis plays an important role in rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) metastasis. With the recent description of CXCR7, a new receptor for SDF-1 that also binds the interferon-inducible T-cell α chemoattractant (ITAC) chemokine, we became interested in the role of the CXCR7-SDF-1/ITAC axis in RMS progression. To address this issue, we evaluated 6 highly metastatic alveolar (A)RMS and 3 less metastatic embryonal (E)RMS cell lines and found that all these cell lines express CXCR7. Although CXCR4 was expressed at a much higher level by highly metastatic ARMS lines, CXCR7 was present at a high level on ERMS lines. We also noticed that CXCR7 expression on RMS cells was downregulated in hypoxic conditions. More importantly, the CXCR7 receptor on RMS cell lines was functional after stimulation with ITAC and SDF-1 as evidenced by mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)p42/44 and AKT phosphorylation as well as CXCR7 internalization, chemotaxis, cell motility and adhesion assays. Similarly to CXCR4, signaling from activated CXCR7 was not associated with increased RMS proliferation or cell survival. Moreover, CXCR7(+) RMS cells responded to SDF-1 and I-TAC in the presence of CXCR4 antagonists (T140, AMD3100). Furthermore, while intravenous injection of RMS cells with overexpressed CXCR7 resulted in increased seeding efficiency of tumor cells to bone marrow, CXCR7 downregulation showed the opposite effect. In conclusion, the CXCR7-SDF-1/ITAC axis is involved in the progression of RMS; targeting of the CXCR4-SDF-1 axis alone without simultaneous blockage of CXCR7 will be an inefficient strategy for inhibiting SDF-1-mediated prometastatic responses of RMS cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CXCR4-SDF-1 signaling is active in rhabdomyosarcoma cells and regulates locomotion, chemotaxis, and adhesion.Blood. 2002 Oct 1;100(7):2597-606. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-01-0031. Blood. 2002. PMID: 12239174
-
Regulation of expression of stromal-derived factor-1 receptors: CXCR4 and CXCR7 in human rhabdomyosarcomas.Mol Cancer Res. 2010 Jan;8(1):1-14. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0259. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Mol Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20068066 Free PMC article.
-
Close correlation between CXCR4 and VEGF expression and frequent CXCR7 expression in rhabdomyosarcoma.Hum Pathol. 2014 Sep;45(9):1900-9. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2014.05.012. Epub 2014 Jun 12. Hum Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25086956
-
The role of stromal-derived factor-1--CXCR7 axis in development and cancer.Eur J Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 25;625(1-3):31-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.04.071. Epub 2009 Oct 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19835865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemokine receptor trio: CXCR3, CXCR4 and CXCR7 crosstalk via CXCL11 and CXCL12.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Feb;24(1):41-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2012.08.007. Epub 2012 Sep 16. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 22989616 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of stromal cell-derived factor 1 and CXCR7 in papillary thyroid carcinoma.Endocr Pathol. 2012 Dec;23(4):247-53. doi: 10.1007/s12022-012-9223-x. Endocr Pathol. 2012. PMID: 23070788
-
Influence of the intensity and loading time of direct current electric field on the directional migration of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Front Med. 2016 Sep;10(3):286-96. doi: 10.1007/s11684-016-0456-9. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Front Med. 2016. PMID: 27324024
-
Metastatic breast cancer cells in the bone marrow microenvironment: novel insights into oncoprotection.Oncol Rev. 2011 Jun 1;5(2):93-102. doi: 10.1007/s12156-010-0071-y. Oncol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21776337 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of a tumor-metastasis-receptive microenvironment as an unwanted and underestimated side effect of treatment by chemotherapy or radiotherapy.J Ovarian Res. 2013 Dec 27;6(1):95. doi: 10.1186/1757-2215-6-95. J Ovarian Res. 2013. PMID: 24373588 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR7 expression is associated with disease-free and disease-specific survival in cervical cancer patients.Br J Cancer. 2012 Apr 24;106(9):1520-5. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2012.110. Br J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22531719 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barr FG, Galili N, Holick J, Biegle JA, Rovera G, Emanuel BS. Rearrangement of the PAX3 paired box gene In the paediatric solid tumore alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Nat Genet. 1993;3:113–7. - PubMed
-
- Kelly KM, Womer RB, Barr FG. 3-FKHR and PAX7-FKHR fusions in rhabdomyosarcoma. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1998;20:517–8. - PubMed
-
- Labura J, Drukala J, Majka M, Tomescu O, Navenot JM, Kucia M, Marquez L, Peiper SC, Barr FG, Janowska-Wieczorek A, Ratajczak MZ. CXCR4-SDF-1 signaling is active in rhabdomyosarcoma cells and regulates locomotion, chemotaxis, and adhesion. Blood. 2002;100:2597–606. - PubMed
-
- Kucia M, Reca R, Miekus K, Wanzeck J, Wojakowski W, Janowska-Wieczorek A, Ratajczak J, Ratajczak MZ. Trafficking of normal stem cells and metastasis of cancer stem cells involve similar mechanisms: pivotal role of the SDF-1-CXCR4 axis. Stem Cells. 2005;23:879–894. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

