Coupling transcriptional and post-transcriptional miRNA regulation in the control of cell fate
- PMID: 20157565
- PMCID: PMC2815735
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.100085
Coupling transcriptional and post-transcriptional miRNA regulation in the control of cell fate
Abstract
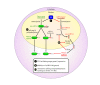
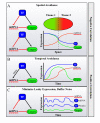
miRNAs function as a critical regulatory layer in development, differentiation, and the maintenance of cell fate. Depletion of miRNAs from embryonic stem cells impairs their differentiation capacity. Total elimination of miRNAs leads to premature senescence in normal cells and tissues through activation of the DNA-damage checkpoint, whereas ablation of miRNAs in cancer cell lines results in an opposite effect, enhancing their tumorigenic potential. Here we compile evidence from the literature that point at miRNAs as key players in the maintenance of genomic integrity and proper cell fate. There is an apparent gap between our understanding of the subtle way by which miRNAs modulate protein levels, and their profound impact on cell fate. We propose that examining miRNAs in the context of the regulatory transcriptional and post-transcriptional networks they are embedded in may provide a broader view of their role in controlling cell fate.
Keywords: Dicer; cancer; genome integrity; miRNA; senescence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Embryonic stem cell microRNAs: defining factors in induced pluripotent (iPS) and cancer (CSC) stem cells?Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009 Sep;4(3):168-77. doi: 10.2174/157488809789057400. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19492978 Review.
-
Implication of the p53-Related miR-34c, -125b, and -203 in the Osteoblastic Differentiation and the Malignant Transformation of Bone Sarcomas.Cells. 2020 Mar 27;9(4):810. doi: 10.3390/cells9040810. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32230926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological functions of microRNAs.Bioorg Khim. 2010 Nov-Dec;36(6):747-52. doi: 10.1134/s1068162010060026. Bioorg Khim. 2010. PMID: 21317939 Review.
-
Repression of transposable-elements - a microRNA anti-cancer defense mechanism?Trends Genet. 2010 Jun;26(6):253-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2010.03.006. Epub 2010 Apr 22. Trends Genet. 2010. PMID: 20417576
-
microRNA(interference) networks are embedded in the gene regulatory networks.Cell Cycle. 2008 Aug 15;7(16):2458-61. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.16.6455. Epub 2008 Aug 17. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18719386
Cited by
-
Understanding microRNA-mediated gene regulatory networks through mathematical modelling.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jul 27;44(13):6019-35. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw550. Epub 2016 Jun 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27317695 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering MicroRNA and Transcription Factor Mediated Regulatory Networks in Glioblastoma.PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(7):e1002488. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002488. Epub 2012 Jul 19. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012. PMID: 22829753 Free PMC article.
-
High-content screen in human pluripotent cells identifies miRNA-regulated pathways controlling pluripotency and differentiation.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Jul 8;10(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1318-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31287022 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis delineates potential signature genes and miRNAs associated with the pathogenesis of asthma.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 7;10(1):13354. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70368-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32770056 Free PMC article.
-
Toward a combinatorial nature of microRNA regulation in human cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Oct;40(19):9404-16. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks759. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22904063 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, Kim SY, Carmell MA, Murchison EP, Alcorn H, Li MZ, Mills AA, Elledge SJ, Anderson KV, Hannon GJ. Dicer is essential for mouse development. Nat Genet. 2003;35:215–217. - PubMed
-
- Wienholds E, Koudijs MJ, van Eeden FJ, Cuppen E, Plasterk RH. The microRNA-producing enzyme Dicer1 is essential for zebrafish development. Nat Genet. 2003;35:217–218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
