Small molecule inhibitors of the neuropilin-1 vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) interaction
- PMID: 20151671
- PMCID: PMC2841442
- DOI: 10.1021/jm901755g
Small molecule inhibitors of the neuropilin-1 vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) interaction
Abstract
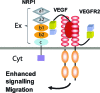
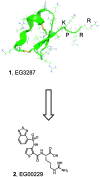
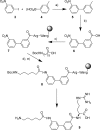
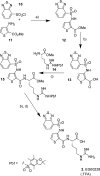
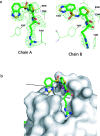
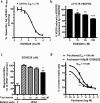
We report the molecular design and synthesis of EG00229, 2, the first small molecule ligand for the VEGF-A receptor neuropilin 1 (NRP1) and the structural characterization of NRP1-ligand complexes by NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography. Mutagenesis studies localized VEGF-A binding in the NRP1 b1 domain and a peptide fragment of VEGF-A was shown to bind at the same site by NMR, providing the basis for small molecule design. Compound 2 demonstrated inhibition of VEGF-A binding to NRP1 and attenuated VEGFR2 phosphorylation in endothelial cells. Inhibition of migration of endothelial cells was also observed. The viability of A549 lung carcinoma cells was reduced by 2, and it increased the potency of the cytotoxic agents paclitaxel and 5-fluorouracil when given in combination. These studies provide the basis for design of specific small molecule inhibitors of ligand binding to NRP1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuropilin-1 antagonism in human carcinoma cells inhibits migration and enhances chemosensitivity.Br J Cancer. 2010 Feb 2;102(3):541-52. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605539. Epub 2010 Jan 19. Br J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20087344 Free PMC article.
-
Autocrine VEGF-VEGFR2-Neuropilin-1 signaling promotes glioma stem-like cell viability and tumor growth.J Exp Med. 2012 Mar 12;209(3):507-20. doi: 10.1084/jem.20111424. Epub 2012 Mar 5. J Exp Med. 2012. PMID: 22393126 Free PMC article.
-
VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) Induces NRP1 (Neuropilin-1) Cleavage via ADAMs (a Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase) 9 and 10 to Generate Novel Carboxy-Terminal NRP1 Fragments That Regulate Angiogenic Signaling.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Aug;38(8):1845-1858. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311118. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29880492 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction of Neuropilin-1 and Neuropilin-2 with tyrosine-kinase receptors for VEGF.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;515:81-90. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0119-0_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002. PMID: 12613545 Review.
-
VEGF-A121a binding to Neuropilins - A concept revisited.Cell Adh Migr. 2018 May 4;12(3):204-214. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2017.1372878. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Cell Adh Migr. 2018. PMID: 29095088 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NRP1 contributes to stemness and potentiates radioresistance via WTAP-mediated m6A methylation of Bcl-2 mRNA in breast cancer.Apoptosis. 2023 Feb;28(1-2):233-246. doi: 10.1007/s10495-022-01784-3. Epub 2022 Nov 4. Apoptosis. 2023. PMID: 36333630
-
Neuropilin-1: a checkpoint target with unique implications for cancer immunology and immunotherapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Jul;8(2):e000967. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000967. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32675311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropilins are multifunctional coreceptors involved in tumor initiation, growth, metastasis and immunity.Oncotarget. 2012 Sep;3(9):921-39. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.626. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 22948112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial VEGFR Coreceptors Neuropilin-1 and Neuropilin-2 Are Essential for Tumor Angiogenesis.Cancer Res Commun. 2022 Dec 14;2(12):1626-1640. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-22-0250. eCollection 2022 Dec. Cancer Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 36970722 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropilin 1 (NRP1) hypomorphism combined with defective VEGF-A binding reveals novel roles for NRP1 in developmental and pathological angiogenesis.Development. 2014 Feb;141(3):556-62. doi: 10.1242/dev.103028. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Development. 2014. PMID: 24401374 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pellet-Many C.; Frankel P.; Jia H.; Zachary I. Neuropilins: structure, function and role in disease. Biochem. J. 2008, 411, 211–226. - PubMed
-
- Kruger R. P.; Aurandt J.; Guan K. L. Semaphorins command cells to move. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 789–800. - PubMed
-
- Pan Q.; Chanthery Y.; Liang W. C.; Stawicki S.; Mak J.; Rathore N.; Tong R. K.; Kowalski J.; Yee S. F.; Pacheco G.; Ross S.; Cheng Z.; Le C. J.; Plowman G.; Peale F.; Koch A. W.; Wu Y.; Bagri A.; Tessier-Lavigne M.; Watts R. J. Blocking neuropilin-1 function has an additive effect with anti-VEGF to inhibit tumor growth. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 53–67. - PubMed
-
- Wells J. A.; McClendon C. L. Reaching for high-hanging fruit in drug discovery at protein−protein interfaces. Nature 2007, 450, 1001–1009. - PubMed
-
- Hajduk P. J.; Huth J. R.; Tse C. Predicting protein druggability. Drug Discovery Today 2005, 10, 1675–1682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

