From basic research to clinical development of MEK1/2 inhibitors for cancer therapy
- PMID: 20149254
- PMCID: PMC2830959
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-8722-3-8
From basic research to clinical development of MEK1/2 inhibitors for cancer therapy
Abstract
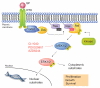
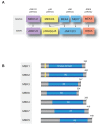
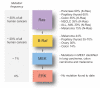
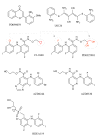
The Ras-dependent Raf/MEK/ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase signaling pathway is a major regulator of cell proliferation and survival. Not surprisingly, hyperactivation of this pathway is frequently observed in human malignancies as a result of aberrant activation of receptor tyrosine kinases or gain-of-function mutations in RAS or RAF genes. Components of the ERK1/2 pathway are therefore viewed as attractive candidates for the development of targeted therapies of cancer. In this article, we briefly review the basic research that has laid the groundwork for the clinical development of small molecules inhibitors of the ERK1/2 pathway. We then present the current state of clinical evaluation of MEK1/2 inhibitors in cancer and discuss challenges ahead.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The clinical development of MEK inhibitors.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014 Jul;11(7):385-400. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2014.83. Epub 2014 May 20. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24840079 Review.
-
MEK1/2 Inhibitors: Molecular Activity and Resistance Mechanisms.Semin Oncol. 2015 Dec;42(6):849-62. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2015.09.023. Epub 2015 Sep 24. Semin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26615130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MEK1 and MEK2 inhibitors and cancer therapy: the long and winding road.Nat Rev Cancer. 2015 Oct;15(10):577-92. doi: 10.1038/nrc4000. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26399658 Review.
-
MEK1/2 inhibitors in the treatment of gynecologic malignancies.Gynecol Oncol. 2014 Apr;133(1):128-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2014.01.008. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Gynecol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24434059 Review.
-
Stamping out RAF and MEK1/2 to inhibit the ERK1/2 pathway: an emerging threat to anticancer therapy.Oncogene. 2016 May 19;35(20):2547-61. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.329. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26364606 Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular targeting in autoimmunity.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012 Dec;12(6):495-510. doi: 10.1007/s11882-012-0307-y. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012. PMID: 23054625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERK1/2 regulation of CD44 modulates oral cancer aggressiveness.Cancer Res. 2012 Jan 1;72(1):365-74. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1831. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22086849 Free PMC article.
-
Cordycepin induces human lung cancer cell apoptosis by inhibiting nitric oxide mediated ERK/Slug signaling pathway.Am J Cancer Res. 2017 Mar 1;7(3):417-432. eCollection 2017. Am J Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28401001 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of tolvaptan-induced toxicity in HepG2 cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2015 Jun 15;95(4):324-36. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.03.015. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25858412 Free PMC article.
-
The MAPK (ERK) Pathway: Investigational Combinations for the Treatment Of BRAF-Mutated Metastatic Melanoma.P T. 2013 Feb;38(2):96-108. P T. 2013. PMID: 23599677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ray LB, Sturgill TW. Characterization of insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein kinase. Rapid isolation and stabilization of a novel serine/threonine kinase from 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:12721–12727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

