Transcriptional control of stem cell maintenance in the Drosophila intestine
- PMID: 20147375
- PMCID: PMC2827683
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.039404
Transcriptional control of stem cell maintenance in the Drosophila intestine
Abstract
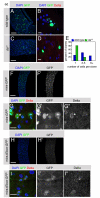
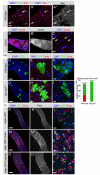
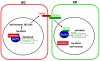
Adult stem cells maintain tissue homeostasis by controlling the proper balance of stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. The adult midgut of Drosophila contains multipotent intestinal stem cells (ISCs) that self-renew and produce differentiated progeny. Control of ISC identity and maintenance is poorly understood. Here we find that transcriptional repression of Notch target genes by a Hairless-Suppressor of Hairless complex is required for ISC maintenance, and identify genes of the Enhancer of split complex [E(spl)-C] as the major targets of this repression. In addition, we find that the bHLH transcription factor Daughterless is essential to maintain ISC identity and that bHLH binding sites promote ISC-specific enhancer activity. We propose that Daughterless-dependent bHLH activity is important for the ISC fate and that E(spl)-C factors inhibit this activity to promote differentiation.
Figures
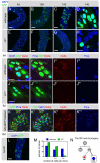
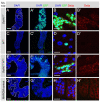
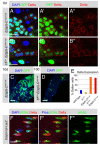
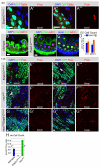
Similar articles
-
Notch signaling downstream target E(spl)mbeta is dispensable for adult midgut homeostasis in Drosophila.Gene. 2015 Apr 10;560(1):89-95. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.01.053. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Gene. 2015. PMID: 25637572
-
Division of Labor: Roles of Groucho and CtBP in Notch-Mediated Lateral Inhibition that Controls Intestinal Stem Cell Differentiation in Drosophila.Stem Cell Reports. 2019 May 14;12(5):1007-1023. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2019.03.005. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Stem Cell Reports. 2019. PMID: 30982741 Free PMC article.
-
The role of p38b MAPK in age-related modulation of intestinal stem cell proliferation and differentiation in Drosophila.Aging (Albany NY). 2009 May 21;1(7):637-51. doi: 10.18632/aging.100054. Aging (Albany NY). 2009. PMID: 20157545 Free PMC article.
-
E(spl): genetic, developmental, and evolutionary aspects of a group of invertebrate Hes proteins with close ties to Notch signaling.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2014;110:217-62. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-405943-6.00006-3. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 25248478 Review.
-
Vertebrate hairy and Enhancer of split related proteins: transcriptional repressors regulating cellular differentiation and embryonic patterning.Oncogene. 2001 Dec 20;20(58):8342-57. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205094. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11840327 Review.
Cited by
-
Intestinal stem cell function in Drosophila and mice.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012 Aug;22(4):354-60. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2012.04.002. Epub 2012 May 19. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012. PMID: 22608824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Notch-mediated suppression of TSC2 expression regulates cell differentiation in the Drosophila intestinal stem cell lineage.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(11):e1003045. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003045. Epub 2012 Nov 8. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23144631 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila models of epithelial stem cells and their niches.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2012 May-Jun;1(3):447-57. doi: 10.1002/wdev.36. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 23801493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and Characterization of Breakpoints and Mutations on Drosophila melanogaster Balancer Chromosomes.G3 (Bethesda). 2020 Nov 5;10(11):4271-4285. doi: 10.1534/g3.120.401559. G3 (Bethesda). 2020. PMID: 32972999 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Intestinal Cell Fate by Dynamic Mitotic Spindle Repositioning Influences Epithelial Homeostasis and Longevity.Cell Rep. 2019 Sep 10;28(11):2807-2823.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.08.014. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31509744 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acar M., Jafar-Nejad H., Giagtzoglou N., Yallampalli S., David G., He Y., Delidakis C., Bellen H. J. (2006). Senseless physically interacts with proneural proteins and functions as a transcriptional co-activator. Development 133, 1979-1989 - PubMed
-
- Bailey A. M., Posakony J. W. (1995). Suppressor of hairless directly activates transcription of enhancer of split complex genes in response to Notch receptor activity. Genes Dev. 9, 2609-2622 - PubMed
-
- Bang A. G., Posakony J. W. (1992). The Drosophila gene Hairless encodes a novel basic protein that controls alternative cell fates in adult sensory organ development. Genes Dev. 6, 1752-1769 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

