Effects of a dual CCR3 and H1-antagonist on symptoms and eosinophilic inflammation in allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 20144207
- PMCID: PMC2833142
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-11-17
Effects of a dual CCR3 and H1-antagonist on symptoms and eosinophilic inflammation in allergic rhinitis
Abstract
Background: The CC-chemokine receptor-3 (CCR3) has emerged as a target molecule for pharmacological intervention in allergic inflammation.
Objective: To examine whether a dual CCR3 and H1-receptor antagonist (AZD3778) affects allergic inflammation and symptoms in allergic rhinitis.
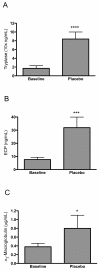
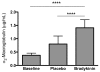
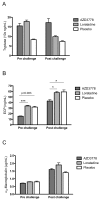
Methods: Patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis were subjected to three seven days' allergen challenge series. Treatment with AZD3778 was given in a placebo and antihistamine-controlled design. Symptoms and nasal peak inspiratory flow (PIF) were monitored in the morning, ten minutes post challenge, and in the evening. Nasal lavages were carried out at the end of each challenge series and alpha2-macroglobulin, ECP, and tryptase were monitored as indices of allergic inflammation.
Results: Plasma levels of AZD3778 were stable throughout the treatment series. AZD3778 and the antihistamine (loratadine) reduced rhinitis symptoms recorded ten minutes post challenge during this period. AZD3778, but not the anti-histamine, also improved nasal PIF ten minutes post challenge. Furthermore, scores for morning and evening nasal symptoms from the last five days of the allergen challenge series showed statistically significant reductions for AZD3778, but not for loratadine. ECP was reduced by AZD3778, but not by loratadine.
Conclusions: AZD3778 exerts anti-eosinophil and symptom-reducing effects in allergic rhinitis and part of this effect can likely be attributed to CCR3-antagonism. The present data are of interest with regard to the potential use of AZD3778 in allergic rhinitis and to the relative importance of eosinophil actions to the symptomatology of allergic rhinitis.
Trial registration: EudraCT No: 2005-002805-21.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Desloratadine reduces allergen challenge-induced mucinous secretion and plasma exudation in allergic rhinitis.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002 Oct;89(4):413-8. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)62044-3. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12392387 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of topical formoterol alone and in combination with budesonide in a pollen season model of allergic rhinitis.Respir Med. 2007 Jun;101(6):1106-12. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2006.11.017. Epub 2007 Jan 9. Respir Med. 2007. PMID: 17215115 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of a nasal glucocorticoid, antileukotriene, and a combination of antileukotriene and antihistamine in the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002 Jun;109(6):949-55. doi: 10.1067/mai.2002.124467. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12063523 Clinical Trial.
-
A review of the efficacy of desloratadine, fexofenadine, and levocetirizine in the treatment of nasal congestion in patients with allergic rhinitis.Clin Ther. 2009 May;31(5):921-44. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.05.017. Clin Ther. 2009. PMID: 19539095 Review.
-
Clinical advantages of dual activity in allergic rhinitis.Allergy. 2000;55 Suppl 64:34-9. doi: 10.1034/j.1398-9995.2000.00805.x. Allergy. 2000. PMID: 11291779 Review.
Cited by
-
Eosinophilic airway inflammation: role in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2016 Jan;7(1):34-51. doi: 10.1177/2040622315609251. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2016. PMID: 26770668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. [corrected]. LXXXIX. Update on the extended family of chemokine receptors and introducing a new nomenclature for atypical chemokine receptors.Pharmacol Rev. 2013 Nov 11;66(1):1-79. doi: 10.1124/pr.113.007724. Print 2014. Pharmacol Rev. 2013. PMID: 24218476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological effects and clinical efficacy of a topical Toll-like receptor 7 agonist in seasonal allergic rhinitis: a parallel group controlled phase IIa study.Inflamm Res. 2015 Nov;64(11):903-15. doi: 10.1007/s00011-015-0873-2. Epub 2015 Sep 5. Inflamm Res. 2015. PMID: 26342289 Clinical Trial.
-
Menthone Inhalation Alleviates Local and Systemic Allergic Inflammation in Ovalbumin-Sensitized and Challenged Asthmatic Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 4;23(7):4011. doi: 10.3390/ijms23074011. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409371 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated intranasal TLR7 stimulation reduces allergen responsiveness in allergic rhinitis.Respir Res. 2012 Jun 22;13(1):53. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-13-53. Respir Res. 2012. PMID: 22726593 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Uguccioni M, Mackay CR, Ochenberger B, Loetscher P, Rhis S, LaRosa GJ, Rao P, Ponath PD, Baggiolini M, Dahinden CA. High expression of the chemokine receptor CCR3 in human blood basophils. Role in activation by eotaxin, MCP-4, and other chemokines. J Clin Invest. 1997;100:1137–1143. doi: 10.1172/JCI119624. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Joubert P, Lajoie-Kadoch S, Labonte I, Gounni AS, Maghni K, Wellemans V, Chakir J, Laviolette M, Hamid Q, Lamkhioued B. CCR3 expression and function in asthmatic airway smooth muscle cells. J Immunol. 2005;175:2702–2708. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

