Mechanism of chromatin remodeling
- PMID: 20142505
- PMCID: PMC2817641
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1000398107
Mechanism of chromatin remodeling
Abstract
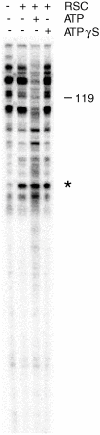
Results from biochemical and structural studies of the RSC chromatin-remodeling complex prompt a proposal for the remodeling mechanism: RSC binding to the nucleosome releases the DNA from the histone surface and initiates DNA translocation (through one or a small number of DNA base pairs); ATP binding completes translocation, and ATP hydrolysis resets the system. Binding energy thus plays a central role in the remodeling process. RSC may disrupt histone-DNA contacts by affecting histone octamer conformation and through extensive interaction with the DNA. Bulging of the DNA from the octamer surface is possible, and twisting is unavoidable, but neither is the basis of remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Distortion of histone octamer core promotes nucleosome mobilization by a chromatin remodeler.Science. 2017 Jan 20;355(6322):eaaa3761. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa3761. Science. 2017. PMID: 28104838 Free PMC article.
-
The synergy between RSC, Nap1 and adjacent nucleosome in nucleosome remodeling.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019 Feb;1862(2):129-140. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2018.11.008. Epub 2018 Dec 26. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019. PMID: 30593928
-
Chromatin remodeling by RSC involves ATP-dependent DNA translocation.Genes Dev. 2002 Aug 15;16(16):2120-34. doi: 10.1101/gad.995002. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 12183366 Free PMC article.
-
ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling and DNA double-strand break repair.Cell Cycle. 2005 Aug;4(8):1011-4. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.8.1887. Epub 2005 Aug 2. Cell Cycle. 2005. PMID: 16082209 Review.
-
Snf2-family proteins: chromatin remodellers for any occasion.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2011 Oct;15(5):649-56. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2011.07.022. Epub 2011 Aug 20. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2011. PMID: 21862382 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Imaging of DNA and Protein-DNA Complexes with Atomic Force Microscopy.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2016;26(1):63-96. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.v26.i1.70. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2016. PMID: 27278886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pyruvate Kinase M2 serves as blockade for nucleosome repositioning and abrogates Chd7 remodeling activity.PLoS One. 2019 Feb 8;14(2):e0211515. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211515. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30735509 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric nucleosomes flank promoters in the budding yeast genome.Genome Res. 2015 Mar;25(3):381-90. doi: 10.1101/gr.182618.114. Epub 2014 Dec 9. Genome Res. 2015. PMID: 25491770 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin remodelers: We are the drivers!!Nucleus. 2016 Jul 3;7(4):388-404. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2016.1211217. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Nucleus. 2016. PMID: 27429206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Charge state of the globular histone core controls stability of the nucleosome.Biophys J. 2010 Sep 8;99(5):1577-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.06.046. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 20816070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lorch Y, Zhang M, Kornberg RD. Histone octamer transfer by a chromatin-remodeling complex. Cell. 1999;96(3):389–392. - PubMed
-
- Whitehouse I, et al. Nucleosome mobilization catalysed by the yeast SWI/SNF complex. Nature. 1999;400(6746):784–787. - PubMed
-
- Saha A, Wittmeyer J, Cairns BR. Chromatin remodelling: The industrial revolution of DNA around histones. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(6):437–447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

