Transcription factors Elk-1 and SRF are engaged in IL1-dependent regulation of ZC3H12A expression
- PMID: 20137095
- PMCID: PMC2829564
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-14
Transcription factors Elk-1 and SRF are engaged in IL1-dependent regulation of ZC3H12A expression
Abstract
Background: MCPIP is a novel CCCH zinc finger protein described as an RNase engaged in the regulation of immune responses. The regulation of expression of the gene coding for MCPIP - ZC3H12A is poorly explored.
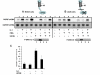
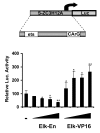
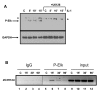
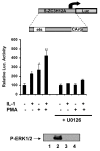
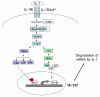
Results: Here we report that the proinflammatory cytokine IL-1beta rapidly induces the synthesis of MCPIP in primary monocyte-derived macrophages and HepG2 cells. This up-regulation takes place through the MAP kinase pathway and following activation of the transcription factor Elk-1. Using a ZC3H12A reporter construct we have shown that a ZC3H12A promoter region, stretching from -76 to +60, mediates activation by IL-1beta. This region contains binding sites for Elk-1 and its partner SRF. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis confirms in vivo binding of both transcription factors to this region of the ZC3H12A promoter.
Conclusions: We conclude that the transcription factor Elk-1 plays an important role in the activation of ZC3H12A expression in response to IL-1beta stimulation.
Figures

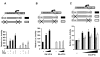
Similar articles
-
Regulatory feedback loop between NF-kappaB and MCP-1-induced protein 1 RNase.FEBS J. 2009 Oct;276(20):5892-905. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07273.x. Epub 2009 Sep 11. FEBS J. 2009. PMID: 19747262
-
Dual Specificity Phosphatase 5, a Specific Negative Regulator of ERK Signaling, Is Induced by Serum Response Factor and Elk-1 Transcription Factor.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 21;10(12):e0145484. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145484. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26691724 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of serum response factor (SRF) with the Elk-1 B box inhibits RhoA-actin signaling to SRF and potentiates transcriptional activation by Elk-1.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Oct;22(20):7083-92. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.20.7083-7092.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12242287 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA degradation by the endoribonuclease Regnase-1/ZC3H12a/MCPIP-1.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jun-Jul;1829(6-7):708-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.03.001. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23500036 Review.
-
Signal-dependent Elk-1 target genes involved in transcript processing and cell migration.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1829(10):1026-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.05.004. Epub 2013 May 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23711433 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) and IL-1 activate translation of overlapping sets of mRNAs, including that of the negative regulator of inflammation, MCPIP1.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 28;288(26):19250-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.452649. Epub 2013 May 8. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23658019 Free PMC article.
-
Elk-1 transcriptionally regulates ZC3H4 expression to promote silica-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Lab Invest. 2020 Jul;100(7):959-973. doi: 10.1038/s41374-020-0419-2. Epub 2020 Mar 26. Lab Invest. 2020. PMID: 32218530
-
The sense behind retroviral anti-sense transcription.Virol J. 2017 Jan 14;14(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12985-016-0667-3. Virol J. 2017. PMID: 28088235 Free PMC article.
-
MCP-induced protein 1 deubiquitinates TRAF proteins and negatively regulates JNK and NF-kappaB signaling.J Exp Med. 2010 Dec 20;207(13):2959-73. doi: 10.1084/jem.20092641. Epub 2010 Nov 29. J Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 21115689 Free PMC article.
-
Regnase-1 in microglia negatively regulates high mobility group box 1-mediated inflammation and neuronal injury.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 5;6:24073. doi: 10.1038/srep24073. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27044405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou L, Azfer A, Niu J, Graham S, Choudhury M, Adamski FM, Younce C, Binkley PF, Kolattukudy PE. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 induces a novel transcription factor that causes cardiac myocyte apoptosis and ventricular dysfunction. Circ Res. 2006;98:1177–85. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000220106.64661.71. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jiang Z, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Qian Y, Matsumoto K, Li X. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor-associated kinase-dependent IL-1-induced signaling complexes phosphorylate TAK1 and TAB2 at the plasma membrane and activate TAK1 in the cytosol. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:7158–67. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.20.7158-7167.2002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

