Vorinostat interferes with the signaling transduction pathway of T-cell receptor and synergizes with phosphoinositide-3 kinase inhibitors in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 20133897
- PMCID: PMC2857191
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2009.013870
Vorinostat interferes with the signaling transduction pathway of T-cell receptor and synergizes with phosphoinositide-3 kinase inhibitors in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Background: Vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, SAHA), an inhibitor of class I and II histone deacetylases, has been approved for the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. In spite of emerging information on the effect of vorinostat in many types of cancer, little is yet known about this drug's mechanism of action, which is essential for its proper use in combination therapy. We investigated alterations in gene expression profile over time in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cells treated with vorinostat. Subsequently, we evaluated inhibitors of PI3K, PIM and HSP90 as potential combination agents in the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
Design and methods: The genes significantly up- or down-regulated by vorinostat over different time periods (2-fold change, false discovery rate corrected P value<0.05) were selected using the short-time series expression miner. Cell viability was assessed in vitro in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cells through measuring intracellular ATP content. Drug interactions were analyzed by the combination index method with CalcuSyn software.
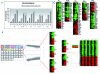
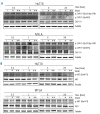
Results: The functional analysis suggests that vorinostat modifies signaling of T-cell receptor, MAPK, and JAK-STAT pathways. The phosphorylation studies of ZAP70 (Tyr319, Tyr493) and its downstream target AKT (Ser473) revealed that vorinostat inhibits phosphorylation of these kinases. With regards to effects on cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cells, combining vorinostat with PI3K inhibitors resulted in synergy while cytotoxic antagonism was observed when vorinostat was combined with HSP90 inhibitor.
Conclusions: These results demonstrate the potential targets of vorinostat, underlining the importance of T-cell receptor signaling inhibition following vorinostat treatment. Additionally, we showed that combination therapies involving histone deacetylase inhibitors and inhibitors of PI3K are potentially efficacious for the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Kinome profiling analysis identified Src pathway as a novel therapeutic target in combination with histone deacetylase inhibitors for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.J Dermatol Sci. 2021 Mar;101(3):194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2021.01.004. Epub 2021 Jan 22. J Dermatol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33531202
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors inhibit metastasis by restoring a tumor suppressive microRNA-150 in advanced cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):7572-7585. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13810. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27935859 Free PMC article.
-
The heat shock protein 90 inhibitor SNX5422 has a synergistic activity with histone deacetylase inhibitors in induction of death of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells.Endocrine. 2016 Feb;51(2):274-82. doi: 10.1007/s12020-015-0706-7. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Endocrine. 2016. PMID: 26219406
-
Vorinostat: A novel therapy for the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2010 May 15;67(10):793-7. doi: 10.2146/ajhp090247. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2010. PMID: 20479100 Review.
-
Drug Insight: histone deacetylase inhibitor-based therapies for cutaneous T-cell lymphomas.Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2008 Dec;5(12):714-26. doi: 10.1038/ncponc1238. Epub 2008 Oct 7. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18839006 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors: emerging mechanisms of resistance.Mol Pharm. 2011 Dec 5;8(6):2021-31. doi: 10.1021/mp200329f. Epub 2011 Oct 7. Mol Pharm. 2011. PMID: 21899343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vorinostat synergizes with ridaforolimus and abrogates the ridaforolimus-induced activation of AKT in synovial sarcoma cells.BMC Res Notes. 2014 Nov 18;7:812. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-812. BMC Res Notes. 2014. PMID: 25406429 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired T cell proliferation by ex vivo BET-inhibition impedes adoptive immunotherapy in a murine melanoma model.Epigenetics. 2020 Jan-Feb;15(1-2):134-144. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2019.1656156. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Epigenetics. 2020. PMID: 31423932 Free PMC article.
-
Quatramer™ encapsulation of dual-targeted PI3-Kδ/HDAC6 inhibitor, HSB-510, suppresses growth of breast cancer.Bioeng Transl Med. 2023 May 12;8(5):e10541. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10541. eCollection 2023 Sep. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37693068 Free PMC article.
-
The role of aurora A and polo-like kinases in high-risk lymphomas.Blood Adv. 2019 Jun 11;3(11):1778-1787. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000232. Blood Adv. 2019. PMID: 31186254 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Girardi M, Heald PW, Wilson LD. The pathogenesis of mycosis fungoides. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(19):1978–88. - PubMed
-
- Wozniak MB, Tracey L, Ortiz-Romero PL, Montes S, Alvarez M, Fraga J, et al. Psoralen plus ultraviolet A +/− interferon-alpha treatment resistance in mycosis fungoides: the role of tumour microenvironment, nuclear transcription factor-kappaB and T-cell receptor pathways. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160(1):92–102. - PubMed
-
- Lamb J, Crawford ED, Peck D, Modell JW, Blat IC, Wrobel MJ, et al. The Connectivity Map: using gene-expression signatures to connect small molecules, genes, and disease. Science. 2006;313(5795):1929–35. - PubMed
-
- Kelly H, Goldberg RM. Systemic therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer: current options, current evidence. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(20):4553–60. - PubMed
-
- O’Connor OA. Targeting histones and proteasomes: new strategies for the treatment of lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(26):6429–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

