Inflammatory cytokine-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in mesenchymal stem cells are critical for immunosuppression
- PMID: 20130212
- PMCID: PMC2881946
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902023
Inflammatory cytokine-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in mesenchymal stem cells are critical for immunosuppression
Abstract
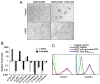
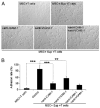
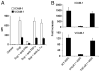
Cell-cell adhesion mediated by ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 is critical for T cell activation and leukocyte recruitment to the inflammation site and, therefore, plays an important role in evoking effective immune responses. However, we found that ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 were critical for mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-mediated immunosuppression. When MSCs were cocultured with T cells in the presence of T cell Ag receptor activation, they significantly upregulated the adhesive capability of T cells due to the increased expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1. By comparing the immunosuppressive effect of MSCs toward various subtypes of T cells and the expression of these adhesion molecules, we found that the greater expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 by MSCs, the greater the immunosuppressive capacity that they exhibited. Furthermore, ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 were found to be inducible by the concomitant presence of IFN-gamma and inflammatory cytokines (TNF-alpha or IL-1). Finally, MSC-mediated immunosuppression was significantly reversed in vitro and in vivo when the adhesion molecules were genetically deleted or functionally blocked, which corroborated the importance of cell-cell contact in immunosuppression by MSCs. Taken together, these findings reveal a novel function of adhesion molecules in immunoregulation by MSCs and provide new insights for the clinical studies of antiadhesion therapies in various immune disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
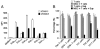

Similar articles
-
Inducible indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 and programmed death ligand 1 expression as the potency marker for mesenchymal stromal cells.Cytotherapy. 2018 May;20(5):639-649. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2018.02.003. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Cytotherapy. 2018. PMID: 29548707
-
Modulated expression of adhesion molecules and galectin-1: role during mesenchymal stromal cell immunoregulatory functions.Exp Hematol. 2010 Oct;38(10):922-32. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2010.05.007. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Exp Hematol. 2010. PMID: 20570633
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and condition media diminish inflammatory adhesion molecules of pulmonary endothelial cells in an ovalbumin-induced asthmatic rat model.Microvasc Res. 2019 Jan;121:63-70. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2018.10.005. Epub 2018 Oct 18. Microvasc Res. 2019. PMID: 30343002
-
Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (CD106) on primary human articular chondrocytes: functional regulation of expression by cytokines and comparison with intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (CD54) and very late activation antigen 2.Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Jul;41(7):1296-305. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199807)41:7<1296::AID-ART21>3.0.CO;2-8. Arthritis Rheum. 1998. PMID: 9663488
-
Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 enhances the therapeutic effects of MSCs in a dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis models by promoting MSCs homing to murine colons and spleens.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Aug 23;10(1):267. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1384-9. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31443680 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Saikosaponin A mediates the inflammatory response by inhibiting the MAPK and NF-κB pathways in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells.Exp Ther Med. 2013 May;5(5):1345-1350. doi: 10.3892/etm.2013.988. Epub 2013 Mar 4. Exp Ther Med. 2013. PMID: 23737876 Free PMC article.
-
How stem cells speak with host immune cells in inflammatory brain diseases.Glia. 2013 Sep;61(9):1379-401. doi: 10.1002/glia.22500. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Glia. 2013. PMID: 23633288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of ibrutinib's effects on the morphology, proliferation, phenotype, viability, and anti-inflammatory potential of adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 28;14(1):19906. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71054-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39191849 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells for cerebral small vessel disease.Regen Ther. 2024 Feb 22;25:377-386. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2023.11.002. eCollection 2024 Mar. Regen Ther. 2024. PMID: 38414558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An efficient protocol to generate placental chorionic plate-derived mesenchymal stem cells with superior proliferative and immunomodulatory properties.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Oct 17;10(1):301. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1405-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31623677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S, Marshak DR. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284:143–147. - PubMed
-
- Le Blanc K, Rasmusson I, Sundberg B, Götherström C, Hassan M, Uzunel M, Ringdén O. Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet. 2004;363:1439–1441. - PubMed
-
- Krampera M, Glennie S, Dyson J, Scott D, Laylor R, Simpson E, Dazzi F. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the response of naive and memory antigen-specific T cells to their cognate peptide. Blood. 2003;101:3722–3729. - PubMed
-
- Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E, Giunti D, Cappiello V, Cazzanti F, Risso M, Gualandi F, Mancardi GL, Pistoia V, Uccelli A. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions. Blood. 2006;107:367–372. - PubMed
-
- Jiang XX, Zhang Y, Liu B, Zhang SX, Wu Y, Yu XD, Mao N. Human mesenchymal stem cells inhibit differentiation and function of monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Blood. 2005;105:4120–4126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

