Interleukin-27 inhibits human osteoclastogenesis by abrogating RANKL-mediated induction of nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 and suppressing proximal RANK signaling
- PMID: 20112358
- PMCID: PMC2822027
- DOI: 10.1002/art.27200
Interleukin-27 inhibits human osteoclastogenesis by abrogating RANKL-mediated induction of nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 and suppressing proximal RANK signaling
Abstract
Objective: Interleukin-27 (IL-27) has stimulatory and regulatory immune functions and is expressed in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovium. This study was undertaken to investigate the effects of IL-27 on human osteoclastogenesis, to determine whether IL-27 can stimulate or attenuate the osteoclast-mediated bone resorption that is a hallmark of RA.
Methods: Osteoclasts were generated from blood-derived human CD14+ cells. The effects of IL-27 on osteoclast formation were evaluated by counting the number of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase-positive multinucleated cells and measuring the expression of osteoclast-related genes. The induction of nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 (NFATc1) and the activation of signaling pathways downstream of RANK were measured by immunoblotting. The expression of key molecules implicated in osteoclastogenesis (NFATc1, RANK, costimulatory receptors, and immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif-harboring adaptor proteins) was measured by real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Murine osteoclast precursors obtained from mouse bone marrow and synovial fluid macrophages derived from RA patients were also tested for their responsiveness to IL-27.
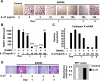
Results: IL-27 inhibited human osteoclastogenesis, suppressed the induction of NFATc1, down-regulated the expression of RANK and triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM-2), and inhibited RANKL-mediated activation of ERK, p38, and NF-kappaB in osteoclast precursors. Synovial fluid macrophages from RA patients were refractory to the effects of IL-27. In contrast to the findings in humans, IL-27 only moderately suppressed murine osteoclastogenesis, and this was likely attributable to low expression of the IL-27 receptor subunit WSX-1 on murine osteoclast precursors.
Conclusion: IL-27 inhibits human osteoclastogenesis by a direct mechanism that suppresses the responses of osteoclast precursors to RANKL. These findings suggest that, in addition to its well-known antiinflammatory effects, IL-27 plays a homeostatic role in restraining bone erosion. This homeostatic function is compromised under conditions of chronic inflammation such as in RA synovitis.
Figures
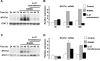

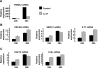
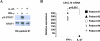
Similar articles
-
Direct inhibition of human RANK+ osteoclast precursors identifies a homeostatic function of IL-1beta.J Immunol. 2010 Nov 15;185(10):5926-34. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001591. Epub 2010 Oct 8. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20935210 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 29 inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via activation of JNK and STAT, and inhibition of NF-κB and NFATc1.Cytokine. 2019 Jan;113:144-154. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.06.032. Epub 2018 Jul 9. Cytokine. 2019. PMID: 30001863
-
Molecular basis of requirement of receptor activator of nuclear factor κB signaling for interleukin 1-mediated osteoclastogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 4;287(19):15728-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.296228. Epub 2012 Mar 13. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22416138 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insight into osteoclast differentiation in osteoimmunology.J Mol Med (Berl). 2005 Mar;83(3):170-9. doi: 10.1007/s00109-004-0612-6. Epub 2005 Jan 26. J Mol Med (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15776286 Review.
-
Current Understanding of RANK Signaling in Osteoclast Differentiation and Maturation.Mol Cells. 2017 Oct;40(10):706-713. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2017.0225. Epub 2017 Oct 17. Mol Cells. 2017. PMID: 29047262 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-27 prevents LPS-induced inflammatory osteolysis by inhibiting osteoclast formation and function.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Mar 15;11(3):1154-1169. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 30972153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B7-H3 regulates osteoclast differentiation via type I interferon-dependent IDO induction.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Oct 20;12(11):971. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04275-6. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34671026 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-27 inhibits ectopic lymphoid-like structure development in early inflammatory arthritis.J Exp Med. 2015 Oct 19;212(11):1793-802. doi: 10.1084/jem.20132307. Epub 2015 Sep 28. J Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26417004 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of cytokines on osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bone remodeling in osteoporosis: a review.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 5;14:1222129. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1222129. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37475866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine-mediated immunomodulation of osteoclastogenesis.Bone. 2022 Nov;164:116540. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2022.116540. Epub 2022 Aug 27. Bone. 2022. PMID: 36031187 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kastelein RA, Hunter CA, Cua DJ. Discovery and biology of IL-23 and IL-27: related but functionally distinct regulators of inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:221–42. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida H, Yoshiyuki M. Regulation of immune responses by interleukin-27. Immunol Rev. 2008;226:234–47. - PubMed
-
- Batten M, Ghilardi N. The biology and therapeutic potential of interleukin 27. J Mol Med. 2007;85(7):661–72. - PubMed
-
- Pflanz S, Timans JC, Cheung J, Rosales R, Kanzler H, Gilbert J, et al. IL-27, a heterodimeric cytokine composed of EBI3 and p28 protein, induces proliferation of naive CD4(+) T cells. Immunity. 2002;16(6):779–90. - PubMed
-
- Pflanz S, Hibbert L, Mattson J, Rosales R, Vaisberg E, Bazan JF, et al. WSX-1 and glycoprotein 130 constitute a signal-transducing receptor for IL-27. J Immunol. 2004;172(4):2225–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

