Glutamate-mediated astrocyte-to-neuron signalling in the rat dorsal horn
- PMID: 20083514
- PMCID: PMC2834942
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.180570
Glutamate-mediated astrocyte-to-neuron signalling in the rat dorsal horn
Abstract
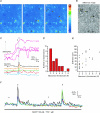
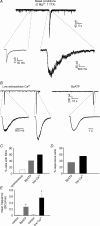
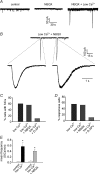
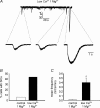
By releasing neuroactive agents, including proinflammatory cytokines, prostaglandins and neurotrophins, microglia and astrocytes are proposed to be involved in nociceptive transmission, especially in conditions of persistent, pathological pain. The specific action on dorsal horn neurons of agents released from astrocytes, such as glutamate, has been, however, poorly investigated. By using patch-clamp and confocal microscope calcium imaging techniques in rat spinal cord slices, we monitored the activity of dorsal horn lamina II neurons following astrocyte activation. Results obtained revealed that stimuli that triggered Ca(2+) elevations in astrocytes, such as the purinergic receptor agonist BzATP and low extracellular Ca(2+), induce in lamina II neurons slow inward currents (SICs). Similarly to SICs triggered by astrocytic glutamate in neurons from other central nervous system regions, these currents (i) are insensitive to tetrodotoxin (TTX), (ii) are blocked by the NMDA receptor (NMDAR) antagonist d-AP5, (iii) lack an AMPA component, and (iv) have slow rise and decay times. Ca(2+) imaging also revealed that astrocytic glutamate evokes NMDAR-mediated episodes of synchronous activity in groups of substantia gelatinosa neurons. Importantly, in a model of peripheral inflammation, the development of thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia was accompanied by a significant increase of spontaneous SICs in dorsal horn neurons. The NMDAR-mediated astrocyte-to-neuron signalling thus represents a novel pathway that may contribute to the control of central sensitization in pathological pain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of P2Y1 receptor in astroglia-to-neuron signaling at dorsal spinal cord.J Neurosci Res. 2009 Sep;87(12):2667-76. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22108. J Neurosci Res. 2009. PMID: 19396875
-
Interferon-gamma potentiates NMDA receptor signaling in spinal dorsal horn neurons via microglia-neuron interaction.Mol Pain. 2016 Apr 18;12:1744806916644927. doi: 10.1177/1744806916644927. Print 2016. Mol Pain. 2016. PMID: 27094552 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte-neuron interaction in the substantia gelatinosa of the spinal cord dorsal horn via P2X7 receptor-mediated release of glutamate and reactive oxygen species.Glia. 2014 Oct;62(10):1671-86. doi: 10.1002/glia.22707. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Glia. 2014. PMID: 24895290
-
Glutamate release from astrocytes as a non-synaptic mechanism for neuronal synchronization in the hippocampus.J Physiol Paris. 2006 Mar-May;99(2-3):98-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jphysparis.2005.12.008. J Physiol Paris. 2006. PMID: 16646155 Review.
-
Bidirectional astrocyte-neuron communication: the many roles of glutamate and ATP.Novartis Found Symp. 2006;276:208-17; discussion 217-21, 233-7, 275-81. doi: 10.1002/9780470032244.ch16. Novartis Found Symp. 2006. PMID: 16805432 Review.
Cited by
-
The computational power of astrocyte mediated synaptic plasticity.Front Comput Neurosci. 2012 Nov 1;6:93. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2012.00093. eCollection 2012. Front Comput Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23125832 Free PMC article.
-
Glia and pain: is chronic pain a gliopathy?Pain. 2013 Dec;154 Suppl 1(0 1):S10-S28. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.06.022. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Pain. 2013. PMID: 23792284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sustained neuronal activity generated by glial plasticity.J Neurosci. 2011 May 25;31(21):7637-47. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5783-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21613477 Free PMC article.
-
Gliotransmission and adenosinergic modulation: insights from mammalian spinal motor networks.J Neurophysiol. 2017 Dec 1;118(6):3311-3327. doi: 10.1152/jn.00230.2017. Epub 2017 Sep 27. J Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28954893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of astrocytes in pain.Neurochem Res. 2012 Nov;37(11):2419-31. doi: 10.1007/s11064-012-0801-6. Epub 2012 May 26. Neurochem Res. 2012. PMID: 22638776 Review.
References
-
- Ahmed Z, Lewis CA, Faber DS. Glutamate stimulates release of Ca2+ from internal stores in astroglia. Brain Research. 1990;516:165–169. - PubMed
-
- Bezzi P, Carmignoto G, Pasti L, Vesce S, Rossi D, Rizzini BL, Pozzan T, Volterra A. Prostaglandins stimulate calcium-dependent glutamate release in astrocytes. Nature. 1998;391:281–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

