Excitatory neurons of the proprioceptive, interoceptive, and arousal hindbrain networks share a developmental requirement for Math1
- PMID: 20080794
- PMCID: PMC2799716
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0911579106
Excitatory neurons of the proprioceptive, interoceptive, and arousal hindbrain networks share a developmental requirement for Math1
Abstract
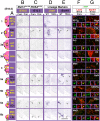
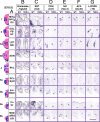
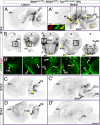
Hindbrain networks important for sensation and arousal contain diverse neuronal populations with distinct projections, yet share specific characteristics such as neurotransmitter expression. The relationship between the function of these neurons, their developmental origin, and the timing of their migration remains unclear. Mice lacking the proneural transcription factor Math1 (Atoh1) lose neurons essential for hearing, balance, and unconscious proprioception. By using a new, inducible Math1(Cre*PR) allele, we found that Math1 is also required for the conscious proprioceptive system, including excitatory projection neurons of the dorsal column nuclei and for vital components of the interoceptive system, such as Barrington's nucleus, that is closely associated with arousal. In addition to specific networks, Math1 lineages shared specific neurotransmitter expression, including glutamate, acetylcholine, somatostatin, corticotropin releasing hormone, and nitric oxide. These findings identify twenty novel Math1 lineages and indicate that the Math1 network functions partly as an interface for conscious (early-born) and unconscious (late-born) proprioceptive inputs to the cortex and cerebellum, respectively. In addition, these data provide previously unsuspected genetic and developmental links between proprioception, interoception, hearing, and arousal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Math1 is essential for the development of hindbrain neurons critical for perinatal breathing.Neuron. 2009 Nov 12;64(3):341-54. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.10.023. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 19914183 Free PMC article.
-
Math1: waiting to inhale.Neuron. 2009 Nov 12;64(3):293-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.10.025. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 19914175
-
Math1 expression redefines the rhombic lip derivatives and reveals novel lineages within the brainstem and cerebellum.Neuron. 2005 Oct 6;48(1):31-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.08.024. Neuron. 2005. PMID: 16202707
-
Neuronal subtype specification in the cerebellum and dorsal hindbrain.Dev Growth Differ. 2012 Apr;54(3):317-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2012.01330.x. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Dev Growth Differ. 2012. PMID: 22404503 Review.
-
Atoh1, an essential transcription factor in neurogenesis and intestinal and inner ear development: function, regulation, and context dependency.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2012 Jun;13(3):281-93. doi: 10.1007/s10162-012-0317-4. Epub 2012 Feb 28. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2012. PMID: 22370966 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Atoh1-lineage gives rise to hair cells and supporting cells within the mammalian cochlea.Dev Biol. 2013 Apr 1;376(1):86-98. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.01.005. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23318633 Free PMC article.
-
Math1 is essential for the development of hindbrain neurons critical for perinatal breathing.Neuron. 2009 Nov 12;64(3):341-54. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.10.023. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 19914183 Free PMC article.
-
The Atoh1-Cre Knock-In Allele Ectopically Labels a Subpopulation of Amacrine Cells and Bipolar Cells in Mouse Retina.eNeuro. 2023 Nov 3;10(11):ENEURO.0307-23.2023. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0307-23.2023. Print 2023 Nov. eNeuro. 2023. PMID: 37923392 Free PMC article.
-
Embryology.Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;154:29-44. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63956-1.00002-3. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29903446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurosensory development of the four brainstem-projecting sensory systems and their integration in the telencephalon.Front Neural Circuits. 2022 Sep 23;16:913480. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2022.913480. eCollection 2022. Front Neural Circuits. 2022. PMID: 36213204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ben-Arie N, et al. Functional conservation of atonal and Math1 in the CNS and PNS. Development. 2000;127:1039–1048. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Arie N, et al. Math1 is essential for genesis of cerebellar granule neurons. Nature. 1997;390:169–172. - PubMed
-
- Wang VY, Rose MF, Zoghbi HY. Math1 expression redefines the rhombic lip derivatives and reveals novel lineages within the brainstem and cerebellum. Neuron. 2005;48:31–43. - PubMed
-
- Machold R, Fishell G. Math1 is expressed in temporally discrete pools of cerebellar rhombic-lip neural progenitors. Neuron. 2005;48:17–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

