Photodynamic therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection in a mouse skin abrasion model
- PMID: 20077489
- PMCID: PMC2820267
- DOI: 10.1002/lsm.20887
Photodynamic therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection in a mouse skin abrasion model
Abstract
Background and objective: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) skin infections are now known to be a common and important problem in the Unites States. The objective of this study was to investigate the efficacy of photodynamic therapy (PDT) for the treatment of MRSA infection in skin abrasion wounds using a mouse model.
Study design/materials and methods: A mouse model of skin abrasion wound infected with MRSA was developed. Bioluminescent strain of MRSA, a derivative of ATCC 33591, was used to allow the real-time monitoring of the extent of infection in mouse wounds. PDT was performed with the combination of a polyethylenimine (PEI)-ce6 photosensitizer (PS) and non-coherent red light. In vivo fluorescence imaging was carried out to evaluate the effect of photobleaching of PS during PDT.
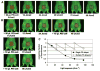
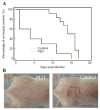
Results: In vivo fluorescence imaging of conjugate PEI-ce6 applied in mice indicated the photobleaching effect of the PS during PDT. PDT induced on average 2.7 log(10) of inactivation of MRSA as judged by loss of bioluminescence in mouse skin abrasion wounds and accelerated the wound healing on average by 8.6 days in comparison to the untreated infected wounds. Photobleaching of PS in the wound was overcome by adding the PS solution in aliquots.
Conclusion: PDT may represent an alternative approach for the treatment of MRSA skin infections.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Blue light eliminates community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in infected mouse skin abrasions.Photomed Laser Surg. 2013 Nov;31(11):531-8. doi: 10.1089/pho.2012.3365. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Photomed Laser Surg. 2013. PMID: 23406384 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy with RLP068 kills methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and improves wound healing in a mouse model of infected skin abrasion PDT with RLP068/Cl in infected mouse skin abrasion.J Biophotonics. 2013 Sep;6(9):733-42. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201200121. Epub 2012 Sep 14. J Biophotonics. 2013. PMID: 22987338 Free PMC article.
-
A novel chlorin derivative Shengtaibufen (STBF) mediated photodynamic therapy combined with iodophor for the treatment of chronic superficial leg wounds infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A retrospective clinical study.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2024 Aug;48:104300. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2024.104300. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2024. PMID: 39097252
-
Anti-microbial photodynamic therapy: useful in the future?Lasers Med Sci. 2007 Jun;22(2):83-91. doi: 10.1007/s10103-006-0409-7. Epub 2006 Nov 21. Lasers Med Sci. 2007. PMID: 17120167 Review.
-
Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:159157. doi: 10.1155/2013/159157. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23555074 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Pulsed 405-nm Light-Emitting Diodes for Antimicrobial Photodynamic Inactivation: Effects of Intensity, Frequency, and Duty Cycle.Photomed Laser Surg. 2017 Mar;35(3):150-156. doi: 10.1089/pho.2016.4179. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Photomed Laser Surg. 2017. PMID: 27759498 Free PMC article.
-
Bioluminescent Models to Evaluate the Efficiency of Light-Based Antibacterial Approaches.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2451:631-669. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2099-1_34. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35505039
-
Emerging strategies for combating Fusobacterium nucleatum in colorectal cancer treatment: Systematic review, improvements and future challenges.Exploration (Beijing). 2023 Dec 22;4(1):20230092. doi: 10.1002/EXP.20230092. eCollection 2024 Feb. Exploration (Beijing). 2023. PMID: 38854496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Beyond antibiotic therapy - Future antiinfective strategies - Update 2017].Unfallchirurg. 2017 Jul;120(7):573-584. doi: 10.1007/s00113-017-0374-6. Unfallchirurg. 2017. PMID: 28643099 Review. German.
-
Blue light eliminates community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in infected mouse skin abrasions.Photomed Laser Surg. 2013 Nov;31(11):531-8. doi: 10.1089/pho.2012.3365. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Photomed Laser Surg. 2013. PMID: 23406384 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Herold BC, Immergluck LC, Maranan MC, Lauderdale DS, Gaskin RE, Boyle-Vavra S, Leitch CD, Daum RS. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in children with no identified predisposing risk. JAMA. 2008;279:593–598. - PubMed
-
- Zervos M. Treatment options for uncomplicated community-acquired skin and soft tissue infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Oral antimicrobial agents. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 2008;9:s29–s34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

