TRPM7 activates m-calpain by stress-dependent stimulation of p38 MAPK and c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- PMID: 20070945
- PMCID: PMC2825087
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.01.014
TRPM7 activates m-calpain by stress-dependent stimulation of p38 MAPK and c-Jun N-terminal kinase
Abstract
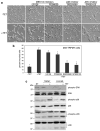
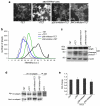
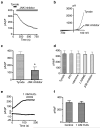
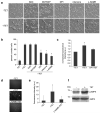
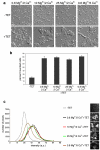
TRPM7 is a Ca(2)(+)-permeant and Mg(2)(+)-permeant ion channel in possession of its own kinase domain. In a previous study, we showed that overexpression of the channel-kinase in HEK-293 cells produced cell rounding and loss of adhesion, which was dependent on the Ca(2+)-dependent protease m-calpain. The TRPM7-elicited change in cell morphology was channel-dependent and occurred without any significant increase in cytosolic Ca(2+). Here we demonstrate that overexpression of TRPM7 increased levels of cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide, causing the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Application of inhibitors of p38 MAPK and JNK blocked TRPM7-induced cell rounding and activation of m-calpain, without affecting the phosphorylation state of the protease. Overexpression of TRPM7 increased intracellular Mg(2+); however, when the concentration of either external Ca(2+) or Mg(2+) was increased to favor the permeation of one divalent cation over the other, a similar increase in cell rounding and calpain activity was detected, indicating that TRPM7-mediated activation of m-calpain is not dependent on the nature of the divalent conducted by the channel. Application of inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase and mitochondrial-derived ROS reduced TRPM7-induced increases in nitric oxide and ROS production, blocked the change in cell morphology, and reduced cellular calpain activity. Collectively, our data reveal that excessive TRPM7 channel activity causes oxidative and nitrosative stresses, producing cell rounding mediated by p38 MAPK/JNK-dependent activation of m-calpain.
(c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
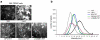
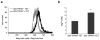
Similar articles
-
A key role for Mg(2+) in TRPM7's control of ROS levels during cell stress.Biochem J. 2012 Aug 1;445(3):441-8. doi: 10.1042/BJ20120248. Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 22587440 Free PMC article.
-
TRPM7 regulates cell adhesion by controlling the calcium-dependent protease calpain.J Biol Chem. 2006 Apr 21;281(16):11260-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M512885200. Epub 2006 Jan 25. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16436382 Free PMC article.
-
TRPM2 contributes to LPS/IFNγ-induced production of nitric oxide via the p38/JNK pathway in microglia.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Feb 7;444(2):212-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.01.022. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24462864
-
The channel-kinase TRPM7, revealing the untold story of Mg(2+) in cellular signaling.Magnes Res. 2014 Jan-Mar;27(1):9-15. doi: 10.1684/mrh.2014.0357. Magnes Res. 2014. PMID: 24752033 Review.
-
Role of TRPM7 kinase in cancer.Cell Calcium. 2021 Jun;96:102400. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2021.102400. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Cell Calcium. 2021. PMID: 33784560 Review.
Cited by
-
Aldosterone signaling through transient receptor potential melastatin 7 cation channel (TRPM7) and its α-kinase domain.Cell Signal. 2013 Nov;25(11):2163-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 6. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23838006 Free PMC article.
-
Stress induces p38 MAPK-mediated phosphorylation and inhibition of Drosha-dependent cell survival.Mol Cell. 2015 Feb 19;57(4):721-734. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.004. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25699712 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Implications of Mammalian Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 7 in the Pathophysiology of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: A Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Oct 12;18(20):10708. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182010708. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34682454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond Ion Homeostasis: Hypomagnesemia, Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin Channel 7, Mitochondrial Function, and Inflammation.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 9;15(18):3920. doi: 10.3390/nu15183920. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37764704 Free PMC article.
-
TRPM7 Induces Mechanistic Target of Rap1b Through the Downregulation of miR-28-5p in Glioma Proliferation and Invasion.Front Oncol. 2019 Dec 17;9:1413. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01413. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31921670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nadler MJS, Hermosura MC, Inabe K, Perraud A-L, Zhu Q, Stokes AJ, Kurosaki T, Kine J-P, Penner R, Scharenberg AM, Fleig A. LTRPC7 is a Mg·ATP-regulated divalent cation channel required for cell viability. Nature. 2001;411:590–595. - PubMed
-
- Runnels LW, Yue L, Clapham DE. TRP-PLIK, a bifunctional protein with kinase and ion channel activities. Science. 2001;291:1043–7. - PubMed
-
- Elizondo MR, Arduini BL, Paulsen J, MacDonald EL, Sabel JL, Henion PD, Cornell RA, Parichy DM. Defective skeletogenesis with kidney stone formation in dwarf zebrafish mutant for trpm7. Curr Biol. 2005;15:667–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

