Structure of a bacterial dynamin-like protein lipid tube provides a mechanism for assembly and membrane curving
- PMID: 20064379
- PMCID: PMC2862293
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.003
Structure of a bacterial dynamin-like protein lipid tube provides a mechanism for assembly and membrane curving
Abstract
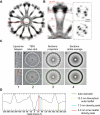
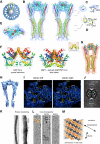
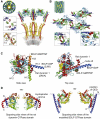
Proteins of the dynamin superfamily mediate membrane fission, fusion, and restructuring events by polymerizing upon lipid bilayers and forcing regions of high curvature. In this work, we show the electron cryomicroscopy reconstruction of a bacterial dynamin-like protein (BDLP) helical filament decorating a lipid tube at approximately 11 A resolution. We fitted the BDLP crystal structure and produced a molecular model for the entire filament. The BDLP GTPase domain dimerizes and forms the tube surface, the GTPase effector domain (GED) mediates self-assembly, and the paddle region contacts the lipids and promotes curvature. Association of BDLP with GMPPNP and lipid induces radical, large-scale conformational changes affecting polymerization. Nucleotide hydrolysis seems therefore to be coupled to polymer disassembly and dissociation from lipid, rather than membrane restructuring. Observed structural similarities with rat dynamin 1 suggest that our results have broad implication for other dynamin family members.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


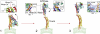
Similar articles
-
Structural basis for GTPase activity and conformational changes of the bacterial dynamin-like protein SynDLP.Cell Rep. 2024 Sep 24;43(9):114657. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114657. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39207903
-
A bacterial dynamin-like protein.Nature. 2006 Dec 7;444(7120):766-9. doi: 10.1038/nature05312. Epub 2006 Nov 22. Nature. 2006. PMID: 17122778
-
Mycobacterial dynamin-like protein IniA mediates membrane fission.Nat Commun. 2019 Aug 29;10(1):3906. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11860-z. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31467269 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamin: functional design of a membrane fission catalyst.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:79-105. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100109-104016. Epub 2011 May 18. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21599493 Review.
-
Dynamin architecture--from monomer to polymer.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2010 Dec;20(6):791-8. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2010.09.011. Epub 2010 Oct 21. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2010. PMID: 20970992 Review.
Cited by
-
Mfn2-dependent fusion pathway of PE-enriched micron-sized vesicles.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 23;121(30):e2313609121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2313609121. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39012824 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative modeling of guanylate binding protein dimers.Protein Sci. 2023 Dec;32(12):e4818. doi: 10.1002/pro.4818. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 37916607 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of IRGB10 oligomerization by GTP hydrolysis.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 29;14:1254415. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1254415. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37705969 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the potential of mitochondrial dynamics as a therapeutic strategy for acute kidney injury.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Aug 11;11:1244313. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1244313. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37635869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural mechanism of mitochondrial membrane remodelling by human OPA1.Nature. 2023 Aug;620(7976):1101-1108. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06441-6. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37612504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen Y.J., Zhang P., Egelman E.H., Hinshaw J.E. The stalk region of dynamin drives the constriction of dynamin tubes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004;11:574–575. - PubMed
-
- Crowther R.A., Henderson R., Smith J.M. MRC image processing programs. J. Struct. Biol. 1996;116:9–16. - PubMed
-
- Danino D., Moon K.H., Hinshaw J.E. Rapid constriction of lipid bilayers by the mechanochemical enzyme dynamin. J. Struct. Biol. 2004;147:259–267. - PubMed
-
- Daumke O., Lundmark R., Vallis Y., Martens S., Butler P.J., McMahon H.T. Architectural and mechanistic insights into an EHD ATPase involved in membrane remodelling. Nature. 2007;449:923–927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

