SPARC suppresses apoptosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis fibroblasts through constitutive activation of beta-catenin
- PMID: 20061390
- PMCID: PMC2832971
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.025684
SPARC suppresses apoptosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis fibroblasts through constitutive activation of beta-catenin
Abstract
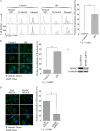
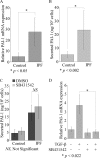
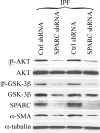
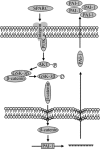
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a poorly understood progressive disease characterized by the accumulation of scar tissue in the lung interstitium. A hallmark of the disease is areas of injury to type II alveolar epithelial cells with attendant accumulation of fibroblasts in areas called fibroblastic foci. In an effort to better characterize the lung fibroblast phenotype in IPF patients, we isolated fibroblasts from patients with IPF and looked for activation of signaling proteins, which could help explain the exaggerated fibrogenic response in IPF. We found that IPF fibroblasts constitutively expressed increased basal levels of SPARC, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), and active beta-catenin compared with control cells. Control of basal PAI-1 expression in IPF fibroblasts was regulated by SPARC-mediated activation of Akt, leading to inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and activation of beta-catenin. Additionally, IPF fibroblasts (but not control fibroblasts) were resistant to plasminogen-induced apoptosis and were sensitized to plasminogen-mediated apoptosis by inhibition of SPARC or beta-catenin. These findings uncover a newly discovered regulatory pathway in IPF fibroblasts that is characterized by elevated SPARC, giving rise to activated beta-catenin, which regulates expression of downstream genes, such as PAI-1, and confers an apoptosis-resistant phenotype. Disruption of this pathway may represent a novel therapeutic target in IPF.
Figures

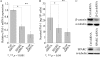
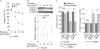
Similar articles
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 suppresses profibrotic responses in fibroblasts from fibrotic lungs.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 10;290(15):9428-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.601815. Epub 2015 Feb 3. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25648892 Free PMC article.
-
Low α(2)β(1) integrin function enhances the proliferation of fibroblasts from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by activation of the β-catenin pathway.Am J Pathol. 2012 Jul;181(1):222-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.03.034. Epub 2012 May 27. Am J Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22642910 Free PMC article.
-
tPA promotes the proliferation of lung fibroblasts and activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Cell Cycle. 2019 Nov;18(22):3137-3146. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1669997. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Cell Cycle. 2019. PMID: 31550972 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular metabolomics of pulmonary fibrosis, from amino acids to lipids.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021 May 1;320(5):C689-C695. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00586.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33471621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Catch your breath: The protective role of the angiotensin AT2 receptor for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Nov;217:115839. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115839. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37778444 Review.
Cited by
-
Systemic sclerosis biomarkers detection in the secretome of TGFβ1-activated primary human lung fibroblasts.J Proteomics. 2021 Jun 30;242:104243. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2021.104243. Epub 2021 Apr 27. J Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 33930553 Free PMC article.
-
WNT/RYK signaling functions as an antiinflammatory modulator in the lung mesenchyme.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jun 14;119(24):e2201707119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2201707119. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35671428 Free PMC article.
-
The lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA1 promotes epithelial cell apoptosis after lung injury.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 Mar;46(3):355-64. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0155OC. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22021336 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis in dermal fibroblasts from patients with diffuse and limited systemic sclerosis reveals common and subset-specific DNA methylation aberrancies.Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Aug;74(8):1612-20. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205303. Epub 2014 May 8. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015. PMID: 24812288 Free PMC article.
-
CEMIP induces TGF-β/Smad signaling to promote keloid development by binding to SPARC.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024 Oct 29;79:100523. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2024.100523. eCollection 2024. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024. PMID: 39481283 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

