A folding zone in the ribosomal exit tunnel for Kv1.3 helix formation
- PMID: 20060838
- PMCID: PMC2865173
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.12.059
A folding zone in the ribosomal exit tunnel for Kv1.3 helix formation
Abstract
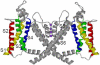
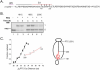
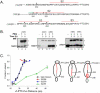
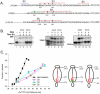
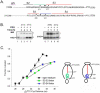
Although it is now clear that protein secondary structure can be acquired early, while the nascent peptide resides within the ribosomal exit tunnel, the principles governing folding of native polytopic proteins have not yet been elucidated. We now report an extensive investigation of native Kv1.3, a voltage-gated K(+) channel, including transmembrane and linker segments synthesized in sequence. These native segments form helices vectorially (N- to C-terminus) only in a permissive vestibule located in the last 20 A of the tunnel. Native linker sequences similarly fold in this vestibule. Finally, secondary structure acquired in the ribosome is retained in the translocon. These findings emerge from accessibility studies of a diversity of native transmembrane and linker sequences and may therefore be applicable to protein biogenesis in general.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

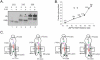
Similar articles
-
Determinants of Helix Formation for a Kv1.3 Transmembrane Segment inside the Ribosome Exit Tunnel.J Mol Biol. 2017 Jun 2;429(11):1722-1732. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.04.022. Epub 2017 May 4. J Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28478285 Free PMC article.
-
Transmembrane segments form tertiary hairpins in the folding vestibule of the ribosome.J Mol Biol. 2014 Jan 9;426(1):185-98. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.09.013. Epub 2013 Sep 17. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24055377 Free PMC article.
-
Structure acquisition of the T1 domain of Kv1.3 during biogenesis.Neuron. 2004 Oct 14;44(2):295-307. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.09.011. Neuron. 2004. PMID: 15473968
-
Ribosome crystallography: catalysis and evolution of peptide-bond formation, nascent chain elongation and its co-translational folding.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Jun;33(Pt 3):488-92. doi: 10.1042/BST0330488. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 15916549 Review.
-
Cotranslational folding--omnia mea mecum porto?Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2001 Jun;33(6):541-53. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(01)00044-9. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11378437 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of SecM-mediated stalling in the ribosome.Biophys J. 2012 Jul 18;103(2):331-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.06.005. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Biophys J. 2012. PMID: 22853911 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and process engineering strategies for enhanced recombinant N-glycoprotein production in bacteria.Microb Cell Fact. 2021 Oct 14;20(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s12934-021-01689-x. Microb Cell Fact. 2021. PMID: 34649588 Free PMC article.
-
A cyclic nucleotide-gated channel mutation associated with canine daylight blindness provides insight into a role for the S2 segment tri-Asp motif in channel biogenesis.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 21;9(2):e88768. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088768. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586388 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of nascent chains with the ribosomal tunnel proteins Rpl4, Rpl17, and Rpl39 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 22;288(47):33697-33707. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.508283. Epub 2013 Sep 26. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24072706 Free PMC article.
-
Birth, life and death of nascent polypeptide chains.Biotechnol J. 2011 Jun;6(6):623-40. doi: 10.1002/biot.201000327. Epub 2011 Apr 29. Biotechnol J. 2011. PMID: 21538896 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nissen P, Hansen J, Ban N, Moore PB, Steitz TA. The structural basis of ribosome activity in peptide bond synthesis. Science. 2000;289:920–930. - PubMed
-
- Kosolapov A, Tu L, Wang J, Deutsch C. Structure Acquisition of the T1 Domain of Kv1.3 During Biogenesis. Neuron. 2004;44:295–307. - PubMed
-
- Lu J, Deutsch C. Secondary structure formation of a transmembrane segment in Kv channels. Biochemistry. 2005;44:8230–8243. - PubMed
-
- Lu J, Deutsch C. Folding zones inside the ribosomal exit tunnel. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005;12:1123–1129. - PubMed
-
- Woolhead CA, McCormick PJ, Johnson AE. Nascent membrane and secretory proteins differ in FRET-detected folding far inside the ribosome and in their exposure to ribosomal proteins. Cell. 2004;116:725–736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

