Cell Separation by Non-Inertial Force Fields in Microfluidic Systems
- PMID: 20046897
- PMCID: PMC2776738
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mechrescom.2008.08.006
Cell Separation by Non-Inertial Force Fields in Microfluidic Systems
Abstract
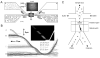
Cell and microparticle separation in microfluidic systems has recently gained significant attention in sample preparations for biological and chemical studies. Microfluidic separation is typically achieved by applying differential forces on the target particles to guide them into different paths. This paper reviews basic concepts and novel designs of such microfluidic separators with emphasis on the use of non-inertial force fields, including dielectrophoretic force, optical gradient force, magnetic force, and acoustic primary radiation force. Comparisons of separation performances with discussions on physiological effects and instrumentation issues toward point-of-care devices are provided as references for choosing appropriate separation methods for various applications.
Figures
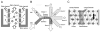
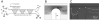


Similar articles
-
Magnetic-based microfluidic platform for biomolecular separation.Biomed Microdevices. 2006 Jun;8(2):151-8. doi: 10.1007/s10544-006-7710-x. Biomed Microdevices. 2006. PMID: 16688574
-
Evaluation of Performance and Tunability of a Co-Flow Inertial Microfluidic Device.Micromachines (Basel). 2020 Mar 10;11(3):287. doi: 10.3390/mi11030287. Micromachines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32164264 Free PMC article.
-
A passive microfluidic device for continuous microparticle enrichment.Electrophoresis. 2019 Mar;40(6):1000-1009. doi: 10.1002/elps.201800454. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Electrophoresis. 2019. PMID: 30488639
-
Dielectrophoretic separation of bioparticles in microdevices: a review.Electrophoresis. 2014 Mar;35(5):691-713. doi: 10.1002/elps.201300424. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Electrophoresis. 2014. PMID: 24338825 Review.
-
A review of dielectrophoretic separation and classification of non-biological particles.Electrophoresis. 2021 Jan;42(1-2):134-152. doi: 10.1002/elps.202000137. Epub 2020 Jul 26. Electrophoresis. 2021. PMID: 32667696 Review.
Cited by
-
Microfluidic separation of live and dead yeast cells using reservoir-based dielectrophoresis.Biomicrofluidics. 2012 Jul 13;6(3):34102. doi: 10.1063/1.4732800. Print 2012 Sep. Biomicrofluidics. 2012. PMID: 23853679 Free PMC article.
-
Separation by nanoparticles plasmonic resonance with low stress in microfluidics channel (analytical and design).IET Nanobiotechnol. 2016 Aug;10(4):230-6. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2015.0067. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27463794 Free PMC article.
-
Curvature-induced dielectrophoresis for continuous separation of particles by charge in spiral microchannels.Biomicrofluidics. 2011 Jun;5(2):24111. doi: 10.1063/1.3599883. Epub 2011 Jun 15. Biomicrofluidics. 2011. PMID: 21792385 Free PMC article.
-
Enabling systems biology approaches through microfabricated systems.Anal Chem. 2013 Oct 1;85(19):8882-94. doi: 10.1021/ac401472y. Anal Chem. 2013. PMID: 23984862 Free PMC article.
-
Inertial focusing in microfluidics.Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2014 Jul 11;16:371-96. doi: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-121813-120704. Epub 2014 May 29. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2014. PMID: 24905880 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Applegate RW, Squier J, Vestad T, Oakey J, Marr DWM. Optical trapping, manipulation, and sorting of cells and colloids in microfluidic systems with diode laser bars. Optics Express. 2004;12:4390–4398. - PubMed
-
- Applegate RW, Squier J, Vestad T, Oakey J, Marr DWM, Bado P, Dugan MA, Said AA. Microfluidic sorting system based on optical waveguide integration and diode laser bar trapping. Lab on a Chip. 2006;6:422–426. - PubMed
-
- Barbulovic-Nad I, Xuan XC, Lee JSH, Li DQ. DC-dielectrophoretic separation of microparticles using an oil droplet obstacle. Lab on a Chip. 2006;6:274–279. - PubMed
-
- Bonner WA, Sweet RG, Hulett HR, Herzenbe La. Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting. Review of Scientific Instruments. 1972;43:404–409. - PubMed
-
- Cheong FC, Sow CH, Wee ATS, Shao P, Bettiol AA, van Kan JA, Watt F. Optical travelator: transport and dynamic sorting of colloidal microspheres with an asymmetrical line optical tweezers. Applied Physics B-Lasers and Optics. 2006;83:121–125.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
