Dynein at the kinetochore: Timing, Interactions and Functions
- PMID: 20045078
- PMCID: PMC2860529
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2009.12.015
Dynein at the kinetochore: Timing, Interactions and Functions
Abstract
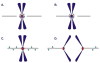
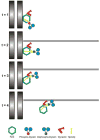
Kinetochores have been proposed to play multiple roles in mitotic chromosome alignment, including initial microtubule (MT) capture, monitoring MT attachments, prometaphase and anaphase chromosome movement and tension generation at metaphase. In addition, kinetochores are essential components of the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), and couple chromosome alignment with SAC silencing at metaphase. Although the molecular details of these activities remain under investigation, cytoplasmic dynein has been implicated in several aspects of MT and SAC regulation. Recent work clarifies the contribution of dynein to MT interactions and to events that drive anaphase onset. This review summarizes these studies and provides new models for dynein function.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microtubule-dependent changes in assembly of microtubule motor proteins and mitotic spindle checkpoint proteins at PtK1 kinetochores.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Jul;12(7):1995-2009. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.7.1995. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11451998 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation regulates targeting of cytoplasmic dynein to kinetochores during mitosis.J Cell Biol. 2008 Dec 1;183(5):819-34. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200804114. Epub 2008 Nov 24. J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 19029334 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetochore dynein is required for chromosome motion and congression independent of the spindle checkpoint.Curr Biol. 2007 Jun 5;17(11):973-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.04.056. Epub 2007 May 17. Curr Biol. 2007. PMID: 17509882 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the kinetochore MAP functions required for stabilizing microtubule attachments to chromosomes during metaphase.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2019 Jun;76(6):398-412. doi: 10.1002/cm.21559. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2019. PMID: 31454167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Merotelic kinetochores in mammalian tissue cells.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005 Mar 29;360(1455):553-68. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2004.1610. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15897180 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rho GTPases as regulators of mitosis and cytokinesis in mammalian cells.Small GTPases. 2014;5:e29770. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.29770. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 24988197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic bonds and polar ejection force distribution explain kinetochore oscillations in PtK1 cells.J Cell Biol. 2013 May 13;201(4):577-93. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201301022. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23671311 Free PMC article.
-
Mitotic spindle proteomics in Chinese hamster ovary cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e20489. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020489. Epub 2011 May 27. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21647379 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Evidence of the Involvement of the Dynein Light Chain DYNLRB2 in Murine Leukemia Virus Infection.J Virol. 2017 Apr 28;91(10):e00129-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00129-17. Print 2017 May 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28250122 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast dynein Dyn2-Pac11 complex is a dynein dimerization/processivity factor: structural and single-molecule characterization.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Aug;24(15):2362-77. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-03-0166. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23761070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rieder CL. Mitosis: towards a molecular understanding of chromosome behavior. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991;3(1):59–66. - PubMed
-
- Musacchio A, Salmon ED. The spindle-assembly checkpoint in space and time. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(5):379–93. - PubMed
-
- Cheeseman IM, Desai A. Molecular architecture of the kinetochore-microtubule interface. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(1):33–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

