Lipolysis in adipocytes
- PMID: 20025992
- PMCID: PMC2835819
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.12.009
Lipolysis in adipocytes
Abstract
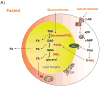
Lipolysis in adipocytes, the hydrolysis of triacylglycerol (TAG) to release fatty acids (FAs) and glycerol for use by other organs, is a unique function of white adipose tissue. Lipolysis in adipocytes occurs at the surface of cytosolic lipid droplets, which have recently gained much attention as dynamic organelles integral to lipid metabolism. Desnutrin/ATGL is now established as a bona fide TAG hydrolase and mutations in human desnutrin/ATGL/PNPLA2, as well as in its activator, comparative gene identification 58, are associated with Neutral Lipid Storage Disease. Furthermore, recent identification of AdPLA as the major adipose phospholipase A(2), has led to the discovery of a dominant autocrine/paracrine regulation of lipolysis through PGE(2). Here, we review emerging concepts in the key players in lipolysis and the regulation of this process. We also examine recent findings in mouse models and humans with alterations/mutations in genes involved in lipolysis and discuss activation of lipolysis in adipocytes as a potential therapeutic target.
2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The skinny on fat: lipolysis and fatty acid utilization in adipocytes.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Nov;20(9):424-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2009.06.002. Epub 2009 Sep 30. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19796963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipocyte lipolysis: from molecular mechanisms of regulation to disease and therapeutics.Biochem J. 2020 Mar 13;477(5):985-1008. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20190468. Biochem J. 2020. PMID: 32168372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of triglyceride metabolism. IV. Hormonal regulation of lipolysis in adipose tissue.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Jul;293(1):G1-4. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00554.2006. Epub 2007 Jan 11. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17218471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Palmitoleic acid (n-7) increases white adipocyte lipolysis and lipase content in a PPARα-dependent manner.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Nov 1;305(9):E1093-102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00082.2013. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 24022867
-
Several agents and pathways regulate lipolysis in adipocytes.Biochimie. 2011 Oct;93(10):1631-40. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.05.018. Epub 2011 May 30. Biochimie. 2011. PMID: 21658426 Review.
Cited by
-
G protein-coupled receptors for energy metabolites as new therapeutic targets.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012 Aug;11(8):603-19. doi: 10.1038/nrd3777. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22790105 Review.
-
Impact of blood perilipin A levels on obesity and metabolic health.BMC Res Notes. 2022 Dec 12;15(1):367. doi: 10.1186/s13104-022-06261-3. BMC Res Notes. 2022. PMID: 36503541 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of LPS and dietary free fatty acids on MCP-1 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and macrophages in vitro.Nutr Diabetes. 2014 Mar 24;4(3):e113. doi: 10.1038/nutd.2014.10. Nutr Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24662749 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of adipose tissue lipolysis and body weight by high-density lipoproteins in mice.Nutr Diabetes. 2014 Feb 24;4(2):e108. doi: 10.1038/nutd.2014.4. Nutr Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24567123 Free PMC article.
-
Studying lipolysis in adipocytes by combining siRNA knockdown and adenovirus-mediated overexpression approaches.Methods Cell Biol. 2013;116:83-105. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-408051-5.00006-1. Methods Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24099289 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brasaemle DL. Thematic review series: adipocyte biology. The perilipin family of structural lipid droplet proteins: stabilization of lipid droplets and control of lipolysis. J Lipid Res. 2007;48:2547–2559. - PubMed
-
- Choi YH, Park S, Hockman S, Zmuda-Trzebiatowska E, Svennelid F, Haluzik M, Gavrilova O, Ahmad F, Pepin L, Napolitano M, Taira M, Sundler F, Stenson Holst L, Degerman E, Manganiello VC. Alterations in regulation of energy homeostasis in cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 3B-null mice. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:3240–3251. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

