A SNP discovery method to assess variant allele probability from next-generation resequencing data
- PMID: 20019143
- PMCID: PMC2813483
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.096388.109
A SNP discovery method to assess variant allele probability from next-generation resequencing data
Abstract
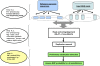
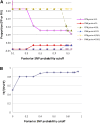
Accurate identification of genetic variants from next-generation sequencing (NGS) data is essential for immediate large-scale genomic endeavors such as the 1000 Genomes Project, and is crucial for further genetic analysis based on the discoveries. The key challenge in single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) discovery is to distinguish true individual variants (occurring at a low frequency) from sequencing errors (often occurring at frequencies orders of magnitude higher). Therefore, knowledge of the error probabilities of base calls is essential. We have developed Atlas-SNP2, a computational tool that detects and accounts for systematic sequencing errors caused by context-related variables in a logistic regression model learned from training data sets. Subsequently, it estimates the posterior error probability for each substitution through a Bayesian formula that integrates prior knowledge of the overall sequencing error probability and the estimated SNP rate with the results from the logistic regression model for the given substitutions. The estimated posterior SNP probability can be used to distinguish true SNPs from sequencing errors. Validation results show that Atlas-SNP2 achieves a false-positive rate of lower than 10%, with an approximately 5% or lower false-negative rate.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SNP calling by sequencing pooled samples.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 Sep 20;13:239. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-239. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22992255 Free PMC article.
-
BAYSIC: a Bayesian method for combining sets of genome variants with improved specificity and sensitivity.BMC Bioinformatics. 2014 Apr 12;15:104. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-104. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24725768 Free PMC article.
-
A statistical method for the detection of variants from next-generation resequencing of DNA pools.Bioinformatics. 2010 Jun 15;26(12):i318-24. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq214. Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20529923 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism-Based Fetal Fraction Estimation of Maternal Plasma Circulating Cell-Free DNA Using Bayesian Hierarchical Models.J Comput Biol. 2018 Sep;25(9):1040-1049. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2018.0056. Epub 2018 Jun 22. J Comput Biol. 2018. PMID: 29932737
-
Review of alignment and SNP calling algorithms for next-generation sequencing data.J Appl Genet. 2016 Feb;57(1):71-9. doi: 10.1007/s13353-015-0292-7. Epub 2015 Jun 9. J Appl Genet. 2016. PMID: 26055432 Review.
Cited by
-
Joint genotyping on the fly: identifying variation among a sequenced panel of inbred lines.Genome Res. 2012 May;22(5):966-74. doi: 10.1101/gr.129122.111. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Genome Res. 2012. PMID: 22367192 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the genome structure of 'Tongil' rice, an important cultivar in the Korean "Green Revolution".Rice (N Y). 2014 Dec;7(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12284-014-0022-5. Epub 2014 Sep 14. Rice (N Y). 2014. PMID: 26224553 Free PMC article.
-
The distribution and mutagenesis of short coding INDELs from 1,128 whole exomes.BMC Genomics. 2015 Feb 28;16(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1333-7. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25765891 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-exome sequencing identifies novel homozygous mutation in NPAS2 in family with nonobstructive azoospermia.Fertil Steril. 2015 Aug;104(2):286-91. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.04.001. Epub 2015 May 5. Fertil Steril. 2015. PMID: 25956372 Free PMC article.
-
ConPADE: genome assembly ploidy estimation from next-generation sequencing data.PLoS Comput Biol. 2015 Apr 16;11(4):e1004229. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004229. eCollection 2015 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015. PMID: 25880203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altshuler D, Pollara VJ, Cowles CR, Van Etten WJ, Baldwin J, Linton L, Lander ES. An SNP map of the human genome generated by reduced representation shotgun sequencing. Nature. 2000;407:513–516. - PubMed
-
- Ewing B, Green P. Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. II. Error probabilities. Genome Res. 1998;8:186–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
