Circulating microvesicles in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia can stimulate marrow stromal cells: implications for disease progression
- PMID: 20018914
- PMCID: PMC2832808
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-242719
Circulating microvesicles in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia can stimulate marrow stromal cells: implications for disease progression
Abstract
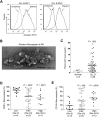
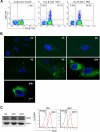
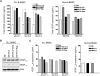
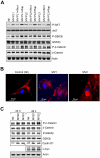
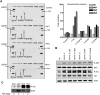
Microvesicles (MVs) released by malignant cancer cells constitute an important part of the tumor microenvironment. They can transfer various messages to target cells and may be critical to disease progression. Here, we demonstrate that MVs circulating in plasma of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients exhibit a phenotypic shift from predominantly platelet derived in early stage to leukemic B-cell derived at advanced stage. Furthermore, the total MV level in CLL was significantly greater compared with healthy subjects. To understand the functional implication, we examined whether MVs can interact and modulate CLL bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) known to provide a "homing and nurturing" environment for CLL B cells. We found that CLL-MV can activate the AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin/p70S6K/hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha axis in CLL-BMSCs with production of vascular endothelial growth factor, a survival factor for CLL B cells. Moreover, MV-mediated AKT activation led to modulation of the beta-catenin pathway and increased expression of cyclin D1 and c-myc in BMSCs. We found MV delivered phospho-receptor tyrosine kinase Axl directly to the BMSCs in association with AKT activation. This study demonstrates the existence of separate MV phenotypes during leukemic disease progression and underscores the important role of MVs in activation of the tumor microenvironment.
Figures
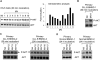
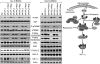
Similar articles
-
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-PDGF receptor interaction activates bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells derived from chronic lymphocytic leukemia: implications for an angiogenic switch.Blood. 2010 Oct 21;116(16):2984-93. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-02-269894. Epub 2010 Jul 6. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20606160 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow stromal cell-derived vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) rather than chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cell-derived VEGF is essential for the apoptotic resistance of cultured CLL cells.Mol Med. 2011;17(7-8):619-27. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2010.00210. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21519633 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of microvesicle generation in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: implication in disease progression.Leukemia. 2017 Feb;31(2):350-360. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.217. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Leukemia. 2017. PMID: 27480387 Free PMC article.
-
Survival and Immunosuppression Induced by Hepatocyte Growth Factor in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Curr Mol Med. 2017;17(1):24-33. doi: 10.2174/1566524017666170220095838. Curr Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28231754 Review.
-
Targeting the B cell receptor pathway in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 2012 Dec;53(12):2362-70. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2012.695781. Leuk Lymphoma. 2012. PMID: 22616724 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic value of miR-155 in individuals with monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis and patients with B chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Blood. 2013 Sep 12;122(11):1891-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-01-478222. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23821659 Free PMC article.
-
VEGF and bFGF gene polymorphisms in Polish patients with B-CLL.Med Oncol. 2013 Mar;30(1):456. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0456-4. Epub 2013 Jan 19. Med Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23335070 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Exosomes in Stemness and Neurodegenerative Diseases-Chemoresistant-Cancer Therapeutics and Phytochemicals.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 17;21(18):6818. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186818. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32957534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression profile of circulating microRNAs as a promising fingerprint for cervical cancer diagnosis and monitoring.Mol Clin Oncol. 2015 Jul;3(4):851-858. doi: 10.3892/mco.2015.560. Epub 2015 May 11. Mol Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26171195 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic stellate cell autophagy inhibits extracellular vesicle release to attenuate liver fibrosis.J Hepatol. 2020 Nov;73(5):1144-1154. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.044. Epub 2020 May 8. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32389810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caligaris-Cappio F. Biology of chronic lymphocytic leukemia [review]. Rev Clin Exp Hematol. 2000;4(1):5–21. - PubMed
-
- Ratajczak J, Wysoczynski M, Hayek F, Janowska-Wieczorek A, Ratajczak MZ. Membrane-derived microvesicles: important and underappreciated mediators of cell-to-cell communication. Leukemia. 2006;20(9):1487–1495. - PubMed
-
- Ratajczak MZ. Microvesicles: from “dust to crown.”. Blood. 2006;108(9):2885–2886.
-
- Janowska-Wieczorek A, Wysoczynski M, Kijowski J, et al. Microvesicles derived from activated platelets induce metastasis and angiogenesis in lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 2005;113(5):752–760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

