Involvement of adiponectin-SIRT1-AMPK signaling in the protective action of rosiglitazone against alcoholic fatty liver in mice
- PMID: 20007851
- PMCID: PMC2838513
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00456.2009
Involvement of adiponectin-SIRT1-AMPK signaling in the protective action of rosiglitazone against alcoholic fatty liver in mice
Abstract
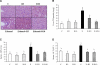
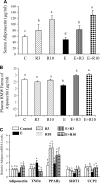
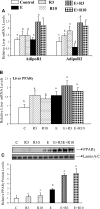
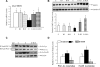
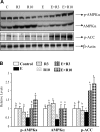
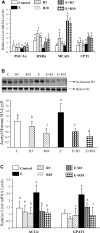
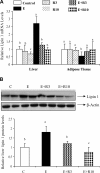
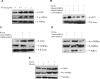
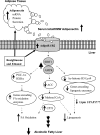
The development of alcoholic fatty liver is associated with reduced adipocyte-derived adiponectin levels, decreased hepatic adiponectin receptors, and deranged hepatic adiponectin signaling in animals. Peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-gamma) plays a key role in the regulation of adiponectin in adipose tissue. The aim of the present study was to test the ability of rosiglitazone, a known PPAR-gamma agonist, to reverse the inhibitory effects of ethanol on adiponectin expression and its hepatic signaling, and to attenuate alcoholic liver steatosis in mice. Mice were fed modified Lieber-DeCarli ethanol-containing liquid diets for 4 wk or pair-fed control diets. Four groups of mice were given a dose of either 3 or 10 mg.kg body wt(-1).day(-1) of rosiglitazone with or without ethanol in their diets for the last 2 wk of the feeding study. Coadministration of rosiglitazone and ethanol increased the expression and circulating levels of adiponectin and enhanced the expression of hepatic adiponectin receptors (AdipoRs) in mice. These increases correlated closely with the activation of a hepatic sirtuin 1 (SIRT1)-AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) signaling system. In concordance with stimulated SIRT1-AMPK signaling, rosiglitazone administration enhanced expression of fatty acid oxidation enzymes, normalized lipin 1 expression, and blocked elevated expression of genes encoding lipogenic enzymes which, in turn, led to increased fatty acid oxidation, reduced lipogenesis, and alleviation of steatosis in the livers of ethanol-fed mice. Enhanced hepatic adiponectin-SIRT1-AMPK signaling contributes, at least in part, to the protective action of rosiglitazone against alcoholic fatty liver in mice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ by rosiglitazone improves lipid homeostasis at the adipose tissue-liver axis in ethanol-fed mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Mar 1;302(5):G548-57. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00342.2011. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22173916 Free PMC article.
-
The adiponectin-SIRT1-AMPK pathway in alcoholic fatty liver disease in the rat.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015 Mar;39(3):424-33. doi: 10.1111/acer.12641. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015. PMID: 25703252
-
Resveratrol alleviates alcoholic fatty liver in mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008 Oct;295(4):G833-42. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.90358.2008. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18755807 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin and alcoholic fatty liver disease.IUBMB Life. 2008 Dec;60(12):790-7. doi: 10.1002/iub.124. IUBMB Life. 2008. PMID: 18709650 Review.
-
Adiponectin: a key adipokine in alcoholic fatty liver.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2009 Aug;234(8):850-9. doi: 10.3181/0902-MR-61. Epub 2009 Jun 2. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2009. PMID: 19491377 Review.
Cited by
-
DSS-induced colitis is associated with adipose tissue dysfunction and disrupted hepatic lipid metabolism leading to hepatosteatosis and dyslipidemia in mice.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 5;11(1):5283. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84761-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33674694 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol administration exacerbates the abnormalities in hepatic lipid oxidation in genetically obese mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013 Jan 1;304(1):G38-47. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00309.2012. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23139221 Free PMC article.
-
Increased dietary fat contributes to dysregulation of the LKB1/AMPK pathway and increased damage in a mouse model of early-stage ethanol-mediated steatosis.J Nutr Biochem. 2013 Aug;24(8):1436-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.12.002. Epub 2013 Mar 1. J Nutr Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23465594 Free PMC article.
-
Carboxylesterase 1 Is Regulated by Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4α and Protects Against Alcohol- and MCD diet-induced Liver Injury.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 14;6:24277. doi: 10.1038/srep24277. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27075303 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Dimorphism in Alcohol Induced Adipose Inflammation Relates to Liver Injury.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 6;11(10):e0164225. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164225. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27711160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bouskila M, Pajvani UB, Scherer PE. Adiponectin: a relevant player in PPARgamma-agonist-mediated improvements in hepatic insulin sensitivity? Int J Obes (Lond) 29: S17–S23, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Brindley DN, Cooling J, Burditt SL, Pritchard PH, Pawson S, Sturton RG. The involvement of glucocorticoids in regulating the activity of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase and the synthesis of triacylglycerols in the liver. Effects of feeding rats with glucose, sorbitol, fructose, glycerol and ethanol. Biochem J 180: 195–199, 1979 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

