The interleukin 6 -174 C/C genotype predicts greater rhinovirus illness
- PMID: 20001857
- PMCID: PMC2943745
- DOI: 10.1086/649559
The interleukin 6 -174 C/C genotype predicts greater rhinovirus illness
Abstract
Background: In adults and children with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection, a polymorphism in the interleukin 6 (IL-6) promoter at position -174 predicts illness magnitude. In addition, polymorphisms in the interleukin 10 (IL-10), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), and interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) genes are associated with immune responsiveness and the frequency of complications. Here, the effect of these polymorphisms on illness and seroconversion during infection with rhinovirus type 39 (RV39) was evaluated.
Methods: Seventy-two adults were genotyped for the selected polymorphisms, experimentally exposed to RV39, and followed to track infection, seroconversion, and symptoms and signs of illness. Regression analysis was used to determine whether these polymorphisms predicted seroconversion and illness magnitude in 57 infected subjects.
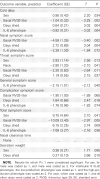
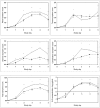
Results: The low-production IL-6 -174 phenotype (C/C genotype) was associated with greater symptom magnitudes, and the IFN-gamma phenotype +874 predicted the frequency of seroconversion. No relationship between the IL-10 or TNF-alpha polymorphisms and any measured outcome was documented. The concentration of IL-6 protein, as measured in nasal wash fluids from subjects, was positively correlated with symptom magnitude, but it was independent of the IL-6 -174 genotypes representing the high- and low-production phenotypes.
Conclusions: These results document statistically significant associations between the IL-6 -174 and IFN-gamma +874 polymorphisms and specific responses to experimental RV39 infection. For the IL-6 -174 polymorphism, the results replicate those for experimental RSV infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest: none reported
Figures
Comment in
-
IL-6 -174 c/c genotype is not conclusively a low IL-6 production phenotype.J Infect Dis. 2011 Jun 15;203(12):1876-8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir181. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21606547 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
IL-6 -174 c/c genotype is not conclusively a low IL-6 production phenotype.J Infect Dis. 2011 Jun 15;203(12):1876-8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir181. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21606547 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Polymorphisms in tumour necrosis factor-alpha, transforming growth factor-beta, interleukin-10, interleukin-6, interferon-gamma, and outcome of hepatitis C virus infection.J Med Virol. 2003 Oct;71(2):212-8. doi: 10.1002/jmv.10472. J Med Virol. 2003. PMID: 12938195
-
Severe preeclampsia: association of genes polymorphisms and maternal cytokines production in Brazilian population.Cytokine. 2015 Feb;71(2):232-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2014.10.021. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 25461403
-
Cytokine gene polymorphisms moderate illness severity in infants with respiratory syncytial virus infection.Hum Immunol. 2003 Mar;64(3):338-44. doi: 10.1016/s0198-8859(02)00827-3. Hum Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12590978
-
Cytokine gene polymorphisms moderate responses to respiratory syncytial virus in adults.Hum Immunol. 2003 Jan;64(1):93-8. doi: 10.1016/s0198-8859(02)00705-x. Hum Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12507818
Cited by
-
Genetic influences on viral-induced cytokine responses in the lung.Mucosal Immunol. 2021 Jan;14(1):14-25. doi: 10.1038/s41385-020-00355-6. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Mucosal Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33184476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis of rhinovirus infection.Curr Opin Virol. 2012 Jun;2(3):287-93. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2012.03.008. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Curr Opin Virol. 2012. PMID: 22542099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Links between Personality and Immune Function.Pers Individ Dif. 2022 Jan;184:111179. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2021.111179. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Pers Individ Dif. 2022. PMID: 34737485 Free PMC article.
-
Immunobiotic Lactobacillus administered post-exposure averts the lethal sequelae of respiratory virus infection.Antiviral Res. 2015 Sep;121:109-19. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.07.001. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Antiviral Res. 2015. PMID: 26145728 Free PMC article.
-
IL-6 -174 c/c genotype is not conclusively a low IL-6 production phenotype.J Infect Dis. 2011 Jun 15;203(12):1876-8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir181. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21606547 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Monto AS. Epidemiology of viral respiratory infections. Am J Med. 2002;112((suppl 6A)):4–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

