Palmitoylation regulates epidermal homeostasis and hair follicle differentiation
- PMID: 19956733
- PMCID: PMC2776530
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000748
Palmitoylation regulates epidermal homeostasis and hair follicle differentiation
Abstract
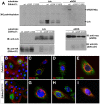
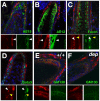
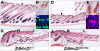
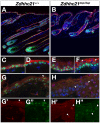
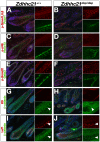
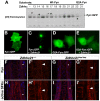
Palmitoylation is a key post-translational modification mediated by a family of DHHC-containing palmitoyl acyl-transferases (PATs). Unlike other lipid modifications, palmitoylation is reversible and thus often regulates dynamic protein interactions. We find that the mouse hair loss mutant, depilated, (dep) is due to a single amino acid deletion in the PAT, Zdhhc21, resulting in protein mislocalization and loss of palmitoylation activity. We examined expression of Zdhhc21 protein in skin and find it restricted to specific hair lineages. Loss of Zdhhc21 function results in delayed hair shaft differentiation, at the site of expression of the gene, but also leads to hyperplasia of the interfollicular epidermis (IFE) and sebaceous glands, distant from the expression site. The specific delay in follicle differentiation is associated with attenuated anagen propagation and is reflected by decreased levels of Lef1, nuclear beta-catenin, and Foxn1 in hair shaft progenitors. In the thickened basal compartment of mutant IFE, phospho-ERK and cell proliferation are increased, suggesting increased signaling through EGFR or integrin-related receptors, with a parallel reduction in expression of the key differentiation factor Gata3. We show that the Src-family kinase, Fyn, involved in keratinocyte differentiation, is a direct palmitoylation target of Zdhhc21 and is mislocalized in mutant follicles. This study is the first to demonstrate a key role for palmitoylation in regulating developmental signals in mammalian tissue homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential sensitivity of epidermal cell subpopulations to beta-catenin-induced ectopic hair follicle formation.Dev Biol. 2010 Jul 1;343(1-2):40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.04.005. Epub 2010 Apr 14. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20398648 Free PMC article.
-
Notch signaling regulates late-stage epidermal differentiation and maintains postnatal hair cycle homeostasis.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 18;6(1):e15842. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015842. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21267458 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal palmitoyl acyl transferases exhibit distinct substrate specificity.FASEB J. 2009 Aug;23(8):2605-15. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-127399. Epub 2009 Mar 19. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 19299482 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles of DHHC-mediated Protein S-palmitoylation in Physiological and Pathophysiological Context.Eur J Cell Biol. 2018 Jun;97(5):319-338. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2018.03.005. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Eur J Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29602512 Review.
-
Protein Palmitoylation by DHHC Protein Family.In: Kittler JT, Moss SJ, editors. The Dynamic Synapse: Molecular Methods in Ionotropic Receptor Biology. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2006. Chapter 5. In: Kittler JT, Moss SJ, editors. The Dynamic Synapse: Molecular Methods in Ionotropic Receptor Biology. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2006. Chapter 5. PMID: 21204476 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
The Protein Acyl Transferase ZDHHC21 Modulates α1 Adrenergic Receptor Function and Regulates Hemodynamics.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Feb;36(2):370-9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.306942. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26715683 Free PMC article.
-
Palmitoylation of Desmoglein 2 Is a Regulator of Assembly Dynamics and Protein Turnover.J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 25;291(48):24857-24865. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.739458. Epub 2016 Oct 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27703000 Free PMC article.
-
S-Palmitoylation of the sodium channel Nav1.6 regulates its activity and neuronal excitability.J Biol Chem. 2020 May 1;295(18):6151-6164. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.012423. Epub 2020 Mar 11. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32161114 Free PMC article.
-
Specificity of transmembrane protein palmitoylation in yeast.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 24;6(2):e16969. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016969. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21383992 Free PMC article.
-
FOXN1 Transcription Factor in Epithelial Growth and Wound Healing.Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Aug 11;37(17):e00110-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00110-17. Print 2017 Sep 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28606930 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smotrys JE, Linder ME. Palmitoylation of intracellular signaling proteins: regulation and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:559–587. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi T, Rumbaugh G, Huganir RL. Differential regulation of AMPA receptor subunit trafficking by palmitoylation of two distinct sites. Neuron. 2005;47:709–723. - PubMed
-
- El Husseini A, Schnell E, Dakoji S, Sweeney N, Zhou Q, et al. Synaptic strength regulated by palmitate cycling on PSD-95. Cell. 2002;108:849–863. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

