Electroporating fields target oxidatively damaged areas in the cell membrane
- PMID: 19956595
- PMCID: PMC2779261
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007966
Electroporating fields target oxidatively damaged areas in the cell membrane
Abstract
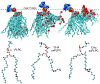
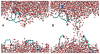
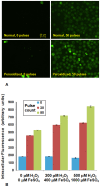
Reversible electropermeabilization (electroporation) is widely used to facilitate the introduction of genetic material and pharmaceutical agents into living cells. Although considerable knowledge has been gained from the study of real and simulated model membranes in electric fields, efforts to optimize electroporation protocols are limited by a lack of detailed understanding of the molecular basis for the electropermeabilization of the complex biomolecular assembly that forms the plasma membrane. We show here, with results from both molecular dynamics simulations and experiments with living cells, that the oxidation of membrane components enhances the susceptibility of the membrane to electropermeabilization. Manipulation of the level of oxidative stress in cell suspensions and in tissues may lead to more efficient permeabilization procedures in the laboratory and in clinical applications such as electrochemotherapy and electrotransfection-mediated gene therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
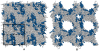
Similar articles
-
Water influx and cell swelling after nanosecond electropermeabilization.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Aug;1828(8):1715-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.03.007. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23500618
-
A molecular dynamic study of cholesterol rich lipid membranes: comparison of electroporation protocols.Bioelectrochemistry. 2014 Dec;100:11-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2014.03.009. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Bioelectrochemistry. 2014. PMID: 24731593
-
Monitoring the molecular composition of live cells exposed to electric pulses via label-free optical methods.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 26;10(1):10471. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67402-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32591612 Free PMC article.
-
The good and the bad of cell membrane electroporation.Acta Chim Slov. 2021 Dec 15;68(4):753-764. doi: 10.17344/acsi.2021.7198. Acta Chim Slov. 2021. PMID: 34918751 Review.
-
Electroporation-based gene therapy: recent evolution in the mechanism description and technology developments.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1121:3-23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-9632-8_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24510808 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidized phosphatidylcholines promote phase separation of cholesterol-sphingomyelin domains.Biophys J. 2012 Jul 18;103(2):247-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.06.017. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Biophys J. 2012. PMID: 22853902 Free PMC article.
-
Modifications of Plasma Membrane Organization in Cancer Cells for Targeted Therapy.Molecules. 2021 Mar 25;26(7):1850. doi: 10.3390/molecules26071850. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33806009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancellation of cellular responses to nanoelectroporation by reversing the stimulus polarity.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Nov;71(22):4431-41. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1626-z. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24748074 Free PMC article.
-
Red blood cell membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles: a novel drug delivery system for antitumor application.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2019 Jul;9(4):675-689. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.01.011. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2019. PMID: 31384529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Nitro-Oxidative Stress on Biomolecules: Part 1-Non-Reactive Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Biomolecules. 2023 Sep 11;13(9):1371. doi: 10.3390/biom13091371. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37759771 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hamilton WA, Sale AJH. Effects of high electric fields on microorganisms. 2. Mechanism of action of lethal effect. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;148:789–800.
-
- Kinosita K, Tsong TY. Voltage-induced pore formation and hemolysis of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977;471:227–242. - PubMed
-
- Harrison RL, Byrne BJ, Tung L. Electroporation-mediated gene transfer in cardiac tissue. FEBS Lett. 1998;435:1–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

