The 5'CL-PCBP RNP complex, 3' poly(A) tail and 2A(pro) are required for optimal translation of poliovirus RNA
- PMID: 19945132
- PMCID: PMC2821882
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.11.006
The 5'CL-PCBP RNP complex, 3' poly(A) tail and 2A(pro) are required for optimal translation of poliovirus RNA
Abstract
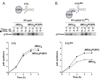
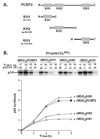
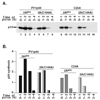
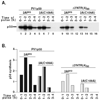
In this study, we showed that the 5'CL-PCBP complex, 3' poly(A) tail and viral protein 2A(pro) are all required for optimal translation of PV RNA. The 2A(pro)-mediated stimulation of translation was observed in the presence or absence of both the 5'CL and the 3' poly(A) tail. Using protein-RNA tethering, we established that the 5'CL-PCBP complex is required for optimal viral RNA translation and identified the KH3 domain of PCBP2 as the functional region. We also showed that the 5'CL-PCBP complex and the 3' poly(A) tail stimulate translation independent of each other. In addition to the independent function of each element, the 5'CL and the 3' poly(A) tail function synergistically to stimulate and prolong translation. These results are consistent with a model in which the 5'CL-PCBP complex interacts with the 3' poly(A)-PABP complex to form a 5'-3' circular complex that facilitates ribosome reloading and stimulates PV RNA translation.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cellular protein modification by poliovirus: the two faces of poly(rC)-binding protein.J Virol. 2007 Sep;81(17):8919-32. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01013-07. Epub 2007 Jun 20. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17581994 Free PMC article.
-
Viral precursor protein P3 and its processed products perform discrete and essential functions in the poliovirus RNA replication complex.Virology. 2015 Nov;485:492-501. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.07.018. Epub 2015 Aug 21. Virology. 2015. PMID: 26303005 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of viral protein 3CD and poly(rC) binding protein with the 5' untranslated region of the poliovirus genome.J Virol. 2000 Mar;74(5):2219-26. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.5.2219-2226.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10666252 Free PMC article.
-
Non-template functions of viral RNA in picornavirus replication.Curr Opin Virol. 2011 Nov;1(5):339-46. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.09.005. Curr Opin Virol. 2011. PMID: 22140418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CVB translation: lessons from the polioviruses.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;323:123-47. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-75546-3_6. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18357768 Review.
Cited by
-
Structures and Corresponding Functions of Five Types of Picornaviral 2A Proteins.Front Microbiol. 2017 Jul 21;8:1373. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01373. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28785248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linking Α to Ω: diverse and dynamic RNA-based mechanisms to regulate gene expression by 5'-to-3' communication.F1000Res. 2016 Aug 19;5:F1000 Faculty Rev-2037. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.7913.1. eCollection 2016. F1000Res. 2016. PMID: 27610229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emergency Services of Viral RNAs: Repair and Remodeling.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018 Mar 14;82(2):e00067-17. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00067-17. Print 2018 Jun. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29540453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple functions of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins in the positive single-stranded RNA virus life cycle.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 2;13:989298. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.989298. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36119073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antagonistic effects of cellular poly(C) binding proteins on vesicular stomatitis virus gene expression.J Virol. 2011 Sep;85(18):9459-71. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05179-11. Epub 2011 Jul 13. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21752917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambros V, Baltimore D. Protein is linked to the 5' end of poliovirus RNA by a phosphodiester linkage to tyrosine. J.Biol.Chem. 1978;253:5263–5266. - PubMed
-
- Andino R, Rieckhof GE, Baltimore D. A functional ribonucleoprotein complex forms around the 5' end of poliovirus RNA. Cell. 1990;63:369–380. - PubMed
-
- Barton DJ, Morasco BJ, Flanegan JB. Assays for poliovirus polymerase, 3Dpol, and authentic RNA replication in HeLa S10 extracts. Methods Enzymol. 1996;275:35–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

