Reversing blood flows act through klf2a to ensure normal valvulogenesis in the developing heart
- PMID: 19924233
- PMCID: PMC2773122
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000246
Reversing blood flows act through klf2a to ensure normal valvulogenesis in the developing heart
Abstract
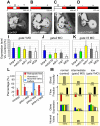
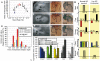
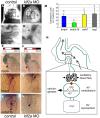
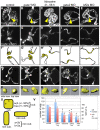
Heart valve anomalies are some of the most common congenital heart defects, yet neither the genetic nor the epigenetic forces guiding heart valve development are well understood. When functioning normally, mature heart valves prevent intracardiac retrograde blood flow; before valves develop, there is considerable regurgitation, resulting in reversing (or oscillatory) flows between the atrium and ventricle. As reversing flows are particularly strong stimuli to endothelial cells in culture, an attractive hypothesis is that heart valves form as a developmental response to retrograde blood flows through the maturing heart. Here, we exploit the relationship between oscillatory flow and heart rate to manipulate the amount of retrograde flow in the atrioventricular (AV) canal before and during valvulogenesis, and find that this leads to arrested valve growth. Using this manipulation, we determined that klf2a is normally expressed in the valve precursors in response to reversing flows, and is dramatically reduced by treatments that decrease such flows. Experimentally knocking down the expression of this shear-responsive gene with morpholine antisense oligonucleotides (MOs) results in dysfunctional valves. Thus, klf2a expression appears to be necessary for normal valve formation. This, together with its dependence on intracardiac hemodynamic forces, makes klf2a expression an early and reliable indicator of proper valve development. Together, these results demonstrate a critical role for reversing flows during valvulogenesis and show how relatively subtle perturbations of normal hemodynamic patterns can lead to both major alterations in gene expression and severe valve dysgenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oscillatory Flow Modulates Mechanosensitive klf2a Expression through trpv4 and trpp2 during Heart Valve Development.Curr Biol. 2015 May 18;25(10):1354-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.03.038. Epub 2015 May 7. Curr Biol. 2015. PMID: 25959969
-
Hemodynamic Forces Sculpt Developing Heart Valves through a KLF2-WNT9B Paracrine Signaling Axis.Dev Cell. 2017 Nov 6;43(3):274-289.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.09.023. Epub 2017 Oct 19. Dev Cell. 2017. PMID: 29056552 Free PMC article.
-
klf2a couples mechanotransduction and zebrafish valve morphogenesis through fibronectin synthesis.Nat Commun. 2016 May 25;7:11646. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11646. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27221222 Free PMC article.
-
Hemodynamics driven cardiac valve morphogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jul;1863(7 Pt B):1760-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.11.014. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26608609 Review.
-
Mechanisms of heart valve development and disease.Development. 2020 Jul 3;147(13):dev183020. doi: 10.1242/dev.183020. Development. 2020. PMID: 32620577 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Computational simulation of hemodynamic-driven growth and remodeling of embryonic atrioventricular valves.Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2012 Nov;11(8):1205-17. doi: 10.1007/s10237-012-0424-5. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2012. PMID: 22869343 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo modulation of endothelial polarization by Apelin receptor signalling.Nat Commun. 2016 Jun 1;7:11805. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11805. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27248505 Free PMC article.
-
Fluid flows and forces in development: functions, features and biophysical principles.Development. 2012 Apr;139(7):1229-45. doi: 10.1242/dev.073593. Development. 2012. PMID: 22395739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for analyzing cardiac phenotypes in the zebrafish embryo.Methods Cell Biol. 2016;134:335-68. doi: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2016.03.002. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Methods Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27312497 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid of light-field and light-sheet imaging to study myocardial function and intracardiac blood flow during zebrafish development.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Jul 6;17(7):e1009175. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009175. eCollection 2021 Jul. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 34228702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beis D, Bartman T, Jin S. W, Scott I. C, D'Amico L. A, et al. Genetic and cellular analyses of zebrafish atrioventricular cushion and valve development. Development. 2005;132:4193–4204. - PubMed
-
- Moorman A. F, Christoffels V. M. Cardiac chamber formation: development, genes, and evolution. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:1223–1267. - PubMed
-
- Chi N. C, Shaw R. M, Jungblut B, Huisken J, Ferrer T, et al. Genetic and physiologic dissection of the vertebrate cardiac conduction system. PLoS Biol. 2008;6:e109. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

