Pharmacokinetics and brain uptake of a genetically engineered bifunctional fusion antibody targeting the mouse transferrin receptor
- PMID: 19921848
- PMCID: PMC2858389
- DOI: 10.1021/mp900235k
Pharmacokinetics and brain uptake of a genetically engineered bifunctional fusion antibody targeting the mouse transferrin receptor
Abstract
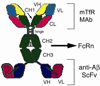
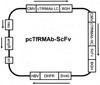
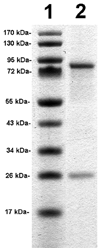
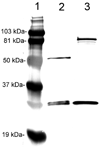
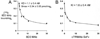
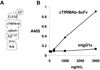
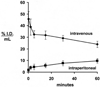
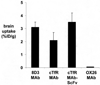
Monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) are potential new therapeutics for brain diseases. However, MAbs do not cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). The present work describes the genetic engineering of a fusion protein composed of a therapeutic single chain Fv (ScFv) antibody and a mouse/rat chimeric MAb against the mouse transferrin receptor (TfR). The TfRMAb acts as a molecular Trojan horse to ferry the therapeutic ScFv across the BBB in vivo in the mouse. The ScFv is fused to the carboxyl terminus of the heavy chain of the chimeric TfRMAb, and this fusion protein is designated cTfRMAb-ScFv. Chinese hamster ovary cells were permanently transfected, and a high secreting cell line in serum free medium was cloned. The cTfRMAb-ScFv fusion protein was purified to homogeneity on gels and Western blotting with protein G affinity chromatography. The cTfRMAb-ScFv fusion protein was bifunctional and bound both the target antigen, as determined by ELISA, and the mouse TfR, as determined with a radio-receptor assay. The cTfRMAb-ScFv fusion protein was radio-iodinated with the Bolton-Hunter reagent, and a pharmacokinetics study in mice showed that the fusion protein was rapidly cleared from blood with a median residence time of 175 +/- 32 min. The fusion protein was avidly taken up by brain with a % injected dose (ID)/g of 3.5 +/- 0.7, as compared to an MAb with no receptor specificity, which was 0.06 +/- 0.01% ID/g. These studies demonstrate that therapeutic MAbs may be re-engineered as fusion proteins with BBB molecular Trojan horses for targeted delivery across the BBB in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IgG-single chain Fv fusion protein therapeutic for Alzheimer's disease: Expression in CHO cells and pharmacokinetics and brain delivery in the rhesus monkey.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2010 Feb 15;105(3):627-35. doi: 10.1002/bit.22576. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2010. PMID: 19816967 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering and expression of a chimeric transferrin receptor monoclonal antibody for blood-brain barrier delivery in the mouse.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2009 Mar 1;102(4):1251-8. doi: 10.1002/bit.22135. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2009. PMID: 18942151 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal antibody-glial-derived neurotrophic factor fusion protein penetrates the blood-brain barrier in the mouse.Drug Metab Dispos. 2010 Apr;38(4):566-72. doi: 10.1124/dmd.109.031534. Epub 2010 Jan 14. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010. PMID: 20075191 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-brain barrier drug delivery of IgG fusion proteins with a transferrin receptor monoclonal antibody.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015 Feb;12(2):207-22. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2014.952627. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 25138991 Review.
-
Reengineering biopharmaceuticals for targeted delivery across the blood-brain barrier.Methods Enzymol. 2012;503:269-92. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-396962-0.00011-2. Methods Enzymol. 2012. PMID: 22230573 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual-targeted magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles reduce brain amyloid-β burden via depolymerization and intestinal metabolism.Theranostics. 2022 Sep 11;12(15):6646-6664. doi: 10.7150/thno.76574. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36185606 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-Brain Barrier and Delivery of Protein and Gene Therapeutics to Brain.Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Jan 10;11:373. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00373. eCollection 2019. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31998120 Free PMC article.
-
Novel treatment strategies for brain tumors and metastases.Pharm Pat Anal. 2014 May;3(3):279-96. doi: 10.4155/ppa.14.19. Pharm Pat Anal. 2014. PMID: 24998288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
pH-responsive antibodies for therapeutic applications.J Biomed Sci. 2021 Jan 22;28(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12929-021-00709-7. J Biomed Sci. 2021. PMID: 33482842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C-fibers may modulate adjacent Aδ-fibers through axon-axon CGRP signaling at nodes of Ranvier in the trigeminal system.J Headache Pain. 2019 Nov 12;20(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s10194-019-1055-3. J Headache Pain. 2019. PMID: 31718551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pardridge WM. Re-engineering biopharmaceuticals for delivery to brain with molecular Trojan horses. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008;19:1327–1338. - PubMed
-
- Pardridge WM, Kang Y-S, Buciak JL, Yang J. Human insulin receptor monoclonal antibody undergoes high affinity binding to human brain capillaries in vitro and rapid transcytosis through the blood-brain barrier in vivo in the primate. Pharm. Res. 1995;12:807–816. - PubMed
-
- Skarlatos S, Yoshikawa T, Pardridge WM. Transport of [125I]transferrin through the rat blood-brain barrier in vivo. Brain Res. 1995;683:164–171. - PubMed
-
- Lee HJ, Engelhardt B, Lesley J, Bickel U, Pardridge WM. Targeting rat anti-mouse transferrin receptor monoclonal antibodies through blood-brain barrier in mouse. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000;292:1048–1052. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

