Mouse Piwi interactome identifies binding mechanism of Tdrkh Tudor domain to arginine methylated Miwi
- PMID: 19918066
- PMCID: PMC2787181
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0911640106
Mouse Piwi interactome identifies binding mechanism of Tdrkh Tudor domain to arginine methylated Miwi
Abstract
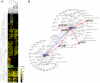
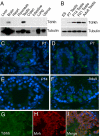
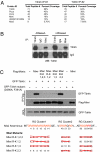
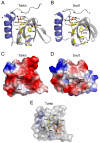
Tudor domains are protein modules that mediate protein-protein interactions, potentially by binding to methylated ligands. A group of germline specific single and multiTudor domain containing proteins (TDRDs) represented by drosophila Tudor and its mammalian orthologs Tdrd1, Tdrd4/RNF17, and Tdrd6 play evolutionarily conserved roles in germinal granule/nuage formation and germ cell specification and differentiation. However, their physiological ligands, and the biochemical and structural basis for ligand recognition, are largely unclear. Here, by immunoprecipitation of endogenous murine Piwi proteins (Miwi and Mili) and proteomic analysis of complexes related to the piRNA pathway, we show that the TDRD group of Tudor proteins are physiological binding partners of Piwi family proteins. In addition, mass spectrometry indicates that arginine residues in RG repeats at the N-termini of Miwi and Mili are methylated in vivo. Notably, we found that Tdrkh/Tdrd2, a novel single Tudor domain containing protein identified in the Miwi complex, is expressed in the cytoplasm of male germ cells and directly associates with Miwi. Mutagenesis studies mapped the Miwi-Tdrkh interaction to the very N-terminal RG/RA repeats of Miwi and showed that the Tdrkh Tudor domain is critical for binding. Furthermore, we have solved the crystal structure of the Tdrkh Tudor domain, which revealed an aromatic binding pocket and negatively charged binding surface appropriate for accommodating methylated arginine. Our findings identify a methylation-directed protein interaction mechanism in germ cells mediated by germline Tudor domains and methylated Piwi family proteins, and suggest a complex mode of regulating the organization and function of Piwi proteins in piRNA silencing pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural basis for arginine methylation-independent recognition of PIWIL1 by TDRD2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Nov 21;114(47):12483-12488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1711486114. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 29118143 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of murine Piwi proteins reveals a role for arginine methylation in specifying interaction with Tudor family members.Genes Dev. 2009 Aug 1;23(15):1749-62. doi: 10.1101/gad.1814809. Epub 2009 Jul 7. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19584108 Free PMC article.
-
MIWI N-terminal RG motif promotes efficient pachytene piRNA production and spermatogenesis independent of LINE1 transposon silencing.PLoS Genet. 2023 Nov 13;19(11):e1011031. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011031. eCollection 2023 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37956204 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of eTudor domain containing TDRD proteins.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 Apr;54(2):119-132. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2019.1603199. Epub 2019 May 3. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31046474 Review.
-
Tudor domain-containing proteins of Drosophila melanogaster.Dev Growth Differ. 2012 Jan;54(1):32-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169x.2011.01308.x. Dev Growth Differ. 2012. PMID: 23741747 Review.
Cited by
-
PIWI Expression and Function in Cancer.Front Genet. 2012 Oct 16;3:204. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00204. eCollection 2012. Front Genet. 2012. PMID: 23087701 Free PMC article.
-
STK31(TDRD8) is dynamically regulated throughout mouse spermatogenesis and interacts with MIWI protein.Histochem Cell Biol. 2012 Mar;137(3):377-89. doi: 10.1007/s00418-011-0897-9. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Histochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22205278
-
PIWI-Interacting RNA Pathway Genes: Potential Biomarkers for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Dis Markers. 2022 Mar 1;2022:3480377. doi: 10.1155/2022/3480377. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35273654 Free PMC article.
-
How does the royal family of Tudor rule the PIWI-interacting RNA pathway?Genes Dev. 2010 Apr 1;24(7):636-46. doi: 10.1101/gad.1899210. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20360382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Readers of histone methylarginine marks.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Aug;1839(8):702-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.02.015. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24583552 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maurer-Stroh S, et al. The Tudor domain “royal family”: Tudor, plant agenet, chromo, PWWP and MBT domains. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003;28:69–74. - PubMed
-
- Adams-Cioaba MA, Min J. Structure and function of histone methylation binding proteins. Biochem Cell Biol. 2009;87:93–105. - PubMed
-
- Cote J, Richard S. Tudor domains bind symmetrical dimethylated arginines. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:28476–28483. - PubMed
-
- Huang Y, Fang J, Bedford MT, Zhang Y, Xu RM. Recognition of histone H3 lysine-4 methylation by the double tudor domain of JMJD2A. Science. 2006;312:748–751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

