Cardioprotection by CaMKII-deltaB is mediated by phosphorylation of heat shock factor 1 and subsequent expression of inducible heat shock protein 70
- PMID: 19910575
- PMCID: PMC2815328
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.210914
Cardioprotection by CaMKII-deltaB is mediated by phosphorylation of heat shock factor 1 and subsequent expression of inducible heat shock protein 70
Abstract
Rationale: Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaMK)II is a multifunctional kinase involved in vital cellular processes such as Ca(2+) handling and cell fate regulation. In mammalian heart, 2 primary CaMKII isoforms, deltaB and deltaC, localize in nuclear and cytosolic compartments, respectively. Although previous studies have established an essential role of CaMKII-deltaC in cardiomyocyte apoptosis, the functional role of the more abundant isoform, CaMKII-deltaB, remains elusive.
Objective: Here, we determined the potential role of CaMKII-deltaB in regulating cardiomyocyte viability and explored the underlying mechanism.
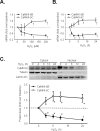
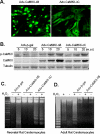
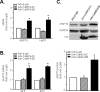
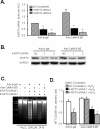
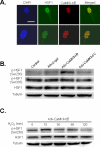
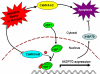
Methods and results: In cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes, the expression of CaMKII-deltaB and CaMKII-deltaC was inversely regulated in response to H2O2-induced oxidative stress with a profound reduction of the former and an increase of the later. Similarly, in vivo ischemia/reperfusion (IR) led to an opposite regulation of these CaMKII isoforms in a rat myocardial IR model. Notably, overexpression of CaMKII-deltaB protected cardiomyocytes against oxidative stress-, hypoxia-, and angiotensin II-induced apoptosis, whereas overexpression of its cytosolic counterpart promoted apoptosis. Using cDNA microarray, real-time PCR and Western blotting, we demonstrated that overexpression of CaMKII-deltaB but not CaMKII-deltaC elevated expression of heat shock protein (HSP)70 family members, including inducible (i)HSP70 and its homolog (Hst70). Moreover, overexpression of CaMKII-deltaB led to phosphorylation and activation of heat shock factor (HSF)1, the primary transcription factor responsible for HSP70 gene regulation. Importantly, gene silencing of iHSP70, but not Hst70, abolished CaMKII-deltaB-mediated protective effect, indicating that only iHSP70 was required for CaMKII-deltaB elicited antiapoptotic signaling.
Conclusions: We conclude that cardiac CaMKII-deltaB and CaMKII-deltaC were inversely regulated in response to oxidative stress and IR injury, and that in contrast to CaMKII-deltaC, CaMKII-deltaB serves as a potent suppressor of cardiomyocyte apoptosis triggered by multiple death-inducing stimuli via phosphorylation of HSF1 and subsequent induction of iHSP70, marking both CaMKII-delta isoforms as promising therapeutic targets for the treatment of ischemic heart disease.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Activation of CaMKIIdeltaC is a common intermediate of diverse death stimuli-induced heart muscle cell apoptosis.J Biol Chem. 2007 Apr 6;282(14):10833-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611507200. Epub 2007 Feb 12. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17296607
-
Heat shock transcription factor-1 inhibits H2O2-induced apoptosis via down-regulation of reactive oxygen species in cardiac myocytes.Mol Cell Biochem. 2011 Jan;347(1-2):21-8. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0608-1. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 20941531
-
Reperfusion causes significant activation of heat shock transcription factor 1 in ischemic rat heart.Circulation. 1996 Nov 1;94(9):2185-92. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.94.9.2185. Circulation. 1996. PMID: 8901670
-
CaMKII, 'jack of all trades' in inflammation during cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2023 Nov;184:48-60. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2023.10.003. Epub 2023 Oct 7. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37813179 Review.
-
CaMKIIδ and cardiomyocyte Ca(2+) signalling new perspectives on splice variant targeting.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015 Dec;42(12):1327-32. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12489. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26361740 Review.
Cited by
-
Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II Regulation by Inhibitor of Receptor Interacting Protein Kinase 3 Alleviates Necroptosis in Glycation End Products-Induced Cardiomyocytes Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 23;23(13):6988. doi: 10.3390/ijms23136988. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35805993 Free PMC article.
-
Calpain 3 and CaMKIIβ signaling are required to induce HSP70 necessary for adaptive muscle growth after atrophy.Hum Mol Genet. 2018 May 1;27(9):1642-1653. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy071. Hum Mol Genet. 2018. PMID: 29528394 Free PMC article.
-
Dusp6 deficiency attenuates neutrophil-mediated cardiac damage in the acute inflammatory phase of myocardial infarction.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 5;13(1):6672. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33631-z. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36335128 Free PMC article.
-
Location matters: clarifying the concept of nuclear and cytosolic CaMKII subtypes.Circ Res. 2011 Dec 9;109(12):1354-62. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.248401. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21998325 Free PMC article.
-
Proteostasis and REDOX state in the heart.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 Jan 1;302(1):H24-37. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00903.2011. Epub 2011 Oct 14. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22003057 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Edman CF, Schulman H. Identification and characterization of delta B-CaM kinase and delta C-CaM kinase from rat heart, two new multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase isoforms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1221:89–101. - PubMed
-
- Baltas LG, Karczewski P, Krause EG. The cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum phospholamban kinase is a distinct delta-CaM kinase isozyme. FEBS Lett. 1995;373:71–75. - PubMed
-
- Hoch B, Meyer R, Hetzer R, Krause EG, Karczewski P. Identification and expression of delta-isoforms of the multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in failing and nonfailing human myocardium. Circ Res. 1999;84:713–721. - PubMed
-
- Hoch B, Wobus AM, Krause EG, Karczewski P. delta-Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II expression pattern in adult mouse heart and cardiogenic differentiation of embryonic stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2000;79:293–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

