BFAST: an alignment tool for large scale genome resequencing
- PMID: 19907642
- PMCID: PMC2770639
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007767
BFAST: an alignment tool for large scale genome resequencing
Abstract
Background: The new generation of massively parallel DNA sequencers, combined with the challenge of whole human genome resequencing, result in the need for rapid and accurate alignment of billions of short DNA sequence reads to a large reference genome. Speed is obviously of great importance, but equally important is maintaining alignment accuracy of short reads, in the 25-100 base range, in the presence of errors and true biological variation.
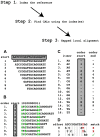
Methodology: We introduce a new algorithm specifically optimized for this task, as well as a freely available implementation, BFAST, which can align data produced by any of current sequencing platforms, allows for user-customizable levels of speed and accuracy, supports paired end data, and provides for efficient parallel and multi-threaded computation on a computer cluster. The new method is based on creating flexible, efficient whole genome indexes to rapidly map reads to candidate alignment locations, with arbitrary multiple independent indexes allowed to achieve robustness against read errors and sequence variants. The final local alignment uses a Smith-Waterman method, with gaps to support the detection of small indels.
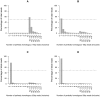
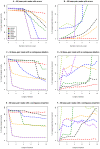
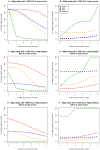
Conclusions: We compare BFAST to a selection of large-scale alignment tools -- BLAT, MAQ, SHRiMP, and SOAP -- in terms of both speed and accuracy, using simulated and real-world datasets. We show BFAST can achieve substantially greater sensitivity of alignment in the context of errors and true variants, especially insertions and deletions, and minimize false mappings, while maintaining adequate speed compared to other current methods. We show BFAST can align the amount of data needed to fully resequence a human genome, one billion reads, with high sensitivity and accuracy, on a modest computer cluster in less than 24 hours. BFAST is available at (http://bfast.sourceforge.net).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform.Bioinformatics. 2009 Jul 15;25(14):1754-60. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324. Epub 2009 May 18. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19451168 Free PMC article.
-
Fast and accurate read alignment for resequencing.Bioinformatics. 2012 Sep 15;28(18):2366-73. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts450. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22811546 Free PMC article.
-
Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform.Bioinformatics. 2010 Mar 1;26(5):589-95. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp698. Epub 2010 Jan 15. Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20080505 Free PMC article.
-
A survey of sequence alignment algorithms for next-generation sequencing.Brief Bioinform. 2010 Sep;11(5):473-83. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbq015. Epub 2010 May 11. Brief Bioinform. 2010. PMID: 20460430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Technology dictates algorithms: recent developments in read alignment.Genome Biol. 2021 Aug 26;22(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s13059-021-02443-7. Genome Biol. 2021. PMID: 34446078 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hoxa2 selectively enhances Meis binding to change a branchial arch ground state.Dev Cell. 2015 Feb 9;32(3):265-77. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.12.024. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Dev Cell. 2015. PMID: 25640223 Free PMC article.
-
From next-generation sequencing alignments to accurate comparison and validation of single-nucleotide variants: the pibase software.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan 7;41(1):e16. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks836. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 22965131 Free PMC article.
-
Promotion of bone morphogenetic protein signaling by tetraspanins and glycosphingolipids.PLoS Genet. 2015 May 15;11(5):e1005221. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005221. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25978409 Free PMC article.
-
The Identification of a Novel Mutant Allele of topoisomerase II in Caenorhabditis elegans Reveals a Unique Role in Chromosome Segregation During Spermatogenesis.Genetics. 2016 Dec;204(4):1407-1422. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.195099. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27707787 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of suppressors of mbk-2/DYRK by whole-genome sequencing.G3 (Bethesda). 2014 Feb 19;4(2):231-41. doi: 10.1534/g3.113.009126. G3 (Bethesda). 2014. PMID: 24347622 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

