Potential role for ESAT6 in dissemination of M. tuberculosis via human lung epithelial cells
- PMID: 19906174
- PMCID: PMC2846543
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06959.x
Potential role for ESAT6 in dissemination of M. tuberculosis via human lung epithelial cells
Abstract
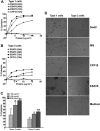
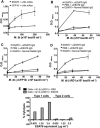
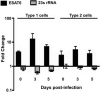
ESAT6 has recently been demonstrated to cause haemolysis and macrophage lysis. Our studies demonstrate that ESAT6 causes cytolysis of type 1 and type 2 pneumocytes. Both types of pneumocytes express membrane laminin, and ESAT6 exhibits dose-dependent binding to both cell types and to purified human laminin. While minimal ESAT6 was detected on the surface of Mycobacterium tuberculosis grown in vitro, exogenously provided ESAT6 specifically associated with the bacterial cell surface, and the bacterium-associated ESAT6 retained its cytolytic ability. esat6 transcripts were upregulated approximately 4- to approximately 13-fold in bacteria replicating in type 1 cells, and approximately 3- to approximately 5 fold in type 2 cells. In vivo, laminin is primarily concentrated at the basolateral surface of pneumocytes where they rest on the basement membrane, which is composed primarily of laminin and collagen. The upregulation of esat6 transcripts in bacteria replicating in pneumocytes, the specific association of ESAT6 with the bacterial surface, the binding of ESAT6 to laminin and the lysis of pneumocytes by free and bacterium-associated ESAT6 together suggest a scenario wherein Mycobacterium tuberculosis replicating in pneumocytes may utilize surface ESAT6 to anchor onto the basolateral laminin-expressing surface of the pneumocytes, and damage the cells and the basement membrane to directly disseminate through the alveolar wall.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phenylalanine-rich peptides potently bind ESAT6, a virulence determinant of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and concurrently affect the pathogen's growth.PLoS One. 2009 Nov 10;4(11):e7615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007615. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19901982 Free PMC article.
-
The CFP10/ESAT6 complex of Mycobacterium tuberculosis may function as a regulator of macrophage cell death at different stages of tuberculosis infection.Med Hypotheses. 2012 Mar;78(3):389-92. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2011.11.022. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Med Hypotheses. 2012. PMID: 22192908
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis ESAT6 induces IFN-β gene expression in Macrophages via TLRs-mediated signaling.Cytokine. 2018 Apr;104:104-109. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.10.006. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Cytokine. 2018. PMID: 29046251
-
The mechanisms and consequences of the extra-pulmonary dissemination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2010 Nov;90(6):361-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2010.08.005. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2010. PMID: 20829117 Review.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Primary Infection and Dissemination: A Critical Role for Alveolar Epithelial Cells.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Aug 21;9:299. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00299. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31497538 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Conserved ESX-1 Substrates EspE and EspF Are Virulence Factors That Regulate Gene Expression.Infect Immun. 2020 Nov 16;88(12):e00289-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00289-20. Print 2020 Nov 16. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32900815 Free PMC article.
-
Silver Nanoparticles for the Therapy of Tuberculosis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Mar 31;15:2231-2258. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S241183. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32280217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of the β-Propeller Protein Gene Rv1057 Reduces ESAT-6 Secretion and Intracellular Growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Curr Microbiol. 2018 Apr;75(4):401-409. doi: 10.1007/s00284-017-1394-8. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Curr Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29134265
-
CD4+ T Responses Other Than Th1 Type Are Preferentially Induced by Latency-Associated Antigens in the State of Latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 29;10:2807. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02807. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31849981 Free PMC article.
-
A Small Protein but with Diverse Roles: A Review of EsxA in Mycobacterium-Host Interaction.Cells. 2021 Jun 30;10(7):1645. doi: 10.3390/cells10071645. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34209120 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bergmann S, Rohde M, Chhatwal GS, Hammerschmidt S. Alpha-enolase of Streptococcus pneumoniae is a plasmin (ogen)-binding protein displayed on the bacterial cell surface. Mol Microbiol. 2001;40:1273–1287. - PubMed
-
- Bermudez LE, Sangari FJ, Kolonoski P, Petrofsky M, Goodman J. The efficiency of translocation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis across a bilayer of epithelial and endothelial cells as a model of the alveolar wall is a consequence of transport within mononuclear phagocytes and invasion of alveolar epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 2002;70:140–146. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berthet FX, Rasmussen PB, Rosenkrands I, Andersen P, Gicquel B. A Mycobacterium tuberculosis operon encoding ESAT-6 and a novel low-molecular-mass culture filtrate protein (CFP-10). Microbiology. 1998;144:3195–3203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

